Question: Using the information in P11-3A, compute the overhead controllable variance and the overhead volume variance. Data From P11-3A Hopkins Clothiers is a small company that
Using the information in P11-3A, compute the overhead controllable variance and the overhead volume variance.
Data From P11-3A
Hopkins Clothiers is a small company that manufactures tall-men’s suits. The company has used a standard cost accounting system. In May 2014, 11,200 suits were produced. The following standard and actual cost data applied to the month of May when normal capacity was 14,000 direct labor hours. All materials purchased were used.
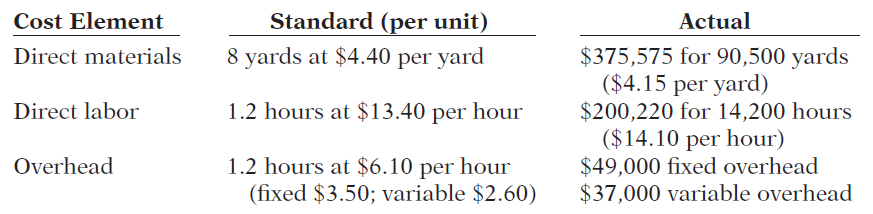
Overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor hours. At normal capacity, budgeted fixed overhead costs were $49,000, and budgeted variable overhead was $36,400.
Instructions
(a) Compute the total, price, and quantity variances for (1) materials and (2) labor.
(b) Compute the total overhead variance.
(c) Which of the materials and labor variances should be investigated if management considers a variance of more than 4% from standard to be significant?
Standard (per unit) Cost Element Direct materials Actual $375,575 for 90,500 yards ($4.15 per yard) $200,220 for 14,200 hours ($14.10 per hour) 8 yards at $4.40 per yard Direct labor 1.2 hours at $13.40 per hour 1.2 hours at $6.10 per hour (fixed $3.50; variable $2.60) $49,000 fixed overhead $37,000 variable overhead Overhead
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Overhead controllable variance Actual Overhead 86000 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
100-B-M-A-S-C (577).docx
120 KBs Word File


