Question: For an ambient separation process where the feed and products are all nonideal liquid solutions at the infinite surroundings temperature, To, (4) of Table 2.1
For an ambient separation process where the feed and products are all nonideal liquid solutions at the infinite surroundings temperature, To, (4) of Table 2.1 for the minimum work of separation reduces toFor the liquid-phase separation at ambient conditions (298 K, 101.3 kPa) of a 35 mol% mixture of acetone (1) in water (2) into 99 mol% acetone and 98 mol% water products, calculate the minimum work in kJ/kmol of feed. Liquid-phase activity coefficients at ambient conditions are correlated reasonably well by the van Laar equations with A12, = 2.0 and A21 = 1.7. What would the minimum rate of work be if acetone and water formed an ideal liquidsolution,?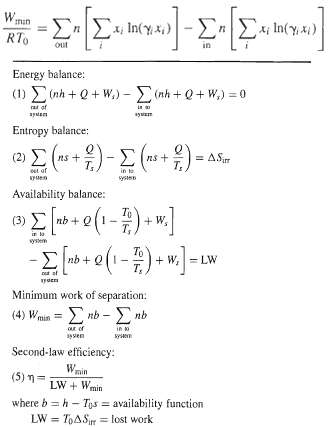
in(y)-n x h(yx) W min RTo out in Energy balance: (1) ot +0+W)-oh+ 0+ W) -0 rat of in Entropy balance: ")- -- (2) E = AS ns + ns + in te systen oet of KPuen Availability balance: (- - . nb + Q (3) + W, T, wystem To + W,= LW nb + Q t at yden Minimum work of separation: (4) Va- 0- (4) Wmin nb ar of apven kyen Second-law efficiency: Wnin LW + Wmin ( 5) - where b = h - Tys = availability function LW = ToASr = lost work
Step by Step Solution
3.25 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Material balance for 1 kmol of feed Let the two products be R and S ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
37-E-C-E-S-P (46).docx
120 KBs Word File


