Question: If X and Y are two identically distributed integrable r.v.s then For any constant c . Now, let g be nonnegative. Then there exist 0
![]()
For any constant c.
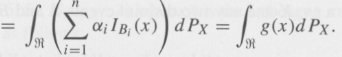
Now, let g be nonnegative. Then there exist 0 £ gn(x) simple †‘ g(x); i.e.,
![]()
Which implies that 0 £
![]()
Simple †‘ g(X) as n†’¥ where Ani = X€“1(Bni). Then
![]()
Whereas
![]()
![]()
For all n, by the previous step. Hence
![]()
Finally, for any g, write g(x) = g+ (x) €“ g€“(x), which implies g(X) = g+(X) €“ g€“ (X). Now, if fWg (X)d P exists, it then follows that either
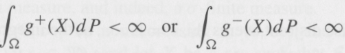
Or both. Since
![]()
And
![]()
By the pervious step, it follows that either
![]()
Or both, respectively, Thus, fÂg(x)d Px exists and
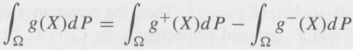
![]()
![]()
Likewise, the existence of fÂg (x)d Px implies the existence of fWg (X)d P and their equality.
E [X1qX\s0] = E [Y IY\so)]
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
In the first place and exist by the Corollary to ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
742-M-S-P (6839).docx
120 KBs Word File


