Question: Proteins can be cleaved specifically at the amide bond on the carboxyl side of methionine residues by reaction with cyanogen bromide, BrC = N. The
Proteins can be cleaved specifically at the amide bond on the carboxyl side of methionine residues by reaction with cyanogen bromide, BrC = N. The reaction occurs in several steps:
(a) The first step is a nucleophilic substitution reaction of the sulfur on the methionine side chain with BrCN to give a cyano sulfonium ion, [R2SCN]+. Show the structure of the product, and propose a mechanism for the reaction.
(b) The second step is an internal SN2 reaction, with the carbonyl oxygen of the methionine residue displacing the positively charged sulfur leaving group and forming a five-membered ring product. Show the structure of the product and the mechanism of its formation.
(c) The third step is a hydrolysis reaction to split the peptide chain. The carboxyl group of the former methionine residue is now part of a lactone (cyclic ester) ring. Show the structure of the lactone product and the mechanism of its formation.
(d) The final step is a hydrolysis of the lactone to give the product shown Show the mechanism of thereaction.
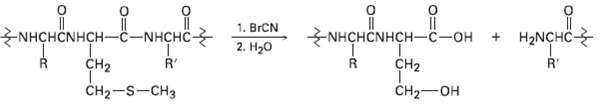
|| 1. BrCN NHCHNHCH-C-OH + H2NHC- NHCHNHCH-C-NHCHC- R' 2. H20 CH2 ' CH2 CH2-S-CH3 CH2 O=U
Step by Step Solution
3.60 Rating (171 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a NHCH I CH CHSCH3 NCBr NHCHC CH CH5CH3 N NHCHC CH CH5CH3 Br The first step is a sub... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
22-C-O-B-M (116).docx
120 KBs Word File


