Question: Perform the indicated operations if the given changes are made in the indicated examples of this section. In Example 1, change the value of X
Perform the indicated operations if the given changes are made in the indicated examples of this section.
In Example 1, change the value of XL to 16.0Ωand then solve the given problem.
Data from Example 1
In the series circuit shown in Fig. 12.25(a), R = 12.0Ωand XL = 5.00Ω. A current of 2.00 A is in the circuit. Find the voltage across each element, the impedance, the voltage across the combination, and the phase angle between the current and the voltage. The voltage across the resistor (between points a and b) is the product of the current and the resistance (V = IR). This means V = (2.00)(12.0) = 24.0 VR. The voltage across the inductor (between points b and c) is the product of the current and the reactance, or VL = (2.00)(5.00) = 10.0 V.
To find the voltage across the combination, between points a and c, we must first find the magnitude of the impedance. Note that the voltage is not the arithmetic sum of VR and VL , as we must account for the phase. By Eq. (12.20), the impedance is (there is no capacitor) Z = 12.0 + 5.00 j with magnitude
![]()
Thus, the magnitude of the voltage across the combination of the resistor and the inductance is |VRL| = (2.00)(13.0) = 26.0 V. The phase angle between the voltage and the current is found by Eq. (12.22). This gives
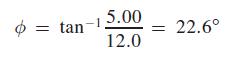
The voltage leads the current by 22.6°, and this is shown in Fig. 12.25(b).
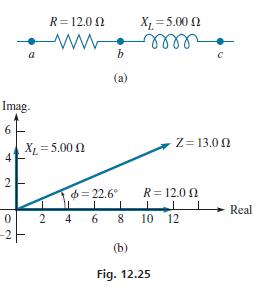
IZI = R + X = (12.0) + (5.00) = 13.0
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (174 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
We are given that R 120and X L 1600 and the current through the circ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


