Researchers have noted that pathological gambling and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) share some similarities such as being unable
Question:
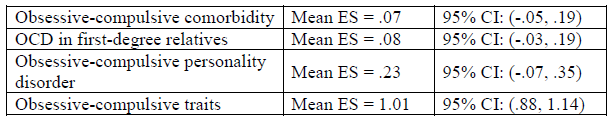
1. Using Cohen€™s guidelines, how would you interpret the mean effect size for the four areas?
2. Based on the 95% CI, what would we conclude regarding the statistical significance of the four mean effect sizes?
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





