Question: Consider the sequence {F n } defined by for n = 0, 1, 2, c. When n = 0, the series is a p-series, and
Consider the sequence {Fn} defined by
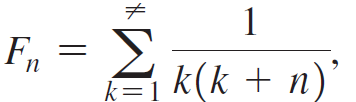
for n = 0, 1, 2, c. When n = 0, the series is a p-series, and we have F0 = π2/6 (Exercises 65 and 66).
a. Explain why {Fn} is a decreasing sequence.
b. Plot {Fn}, for n = 1, 2, . . . , 20.
c. Based on your experiments, make a conjecture about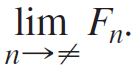
Data from Exercise 65
The Riemann zeta function is the subject of extensive research and is associated with several renowned unsolved problems. It is defined by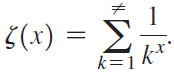 When x is a real number, the zeta function becomes a p-series. For even positive integers p, the value of
When x is a real number, the zeta function becomes a p-series. For even positive integers p, the value of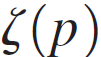 is known exactly. For example,
is known exactly. For example,
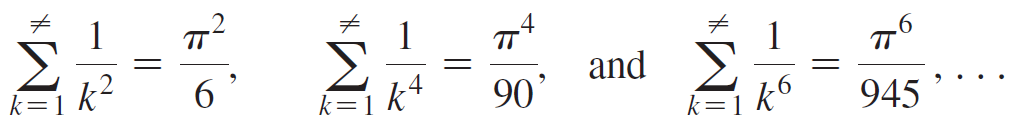
Use the estimation techniques described in the text to approximate 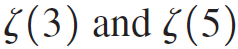 (whose values are not known exactly) with a remainder less than 10-3.
(whose values are not known exactly) with a remainder less than 10-3.
Data from Exercise 66
In 1734, Leonhard Euler informally proved that 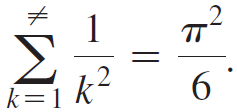 An elegant proof is outlined here that uses the inequality
An elegant proof is outlined here that uses the inequality
cot2 x 2 2 x (provided that 0
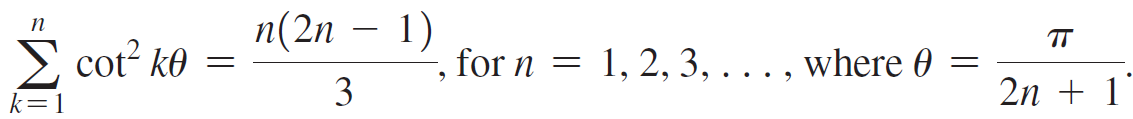
- k(k + n) k=1 lim Fp. >#
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a F is a decreasing sequence because each ter... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


