Question: Refer to Problem 3.42 and exact tests using X 2 with Hα: Ï 1 Ï 2 . Explain why the unconditional P-value, evaluated at Ï
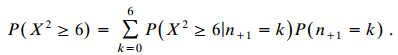
Thus, the unconditional P-value of 1/32 is a weighted average of the Fisher P-value for the observed column margins and P-values of 0 corresponding to the impossibility of getting results as extreme as observed if other margins had occurred i.e.
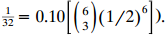
The Fisher quote in Section 3.5.6 gave his view about this.
Data from Prob. 3.42:
A contingency table for two independent binomial variable has counts (3, 0 / 0, 3) by row. For H0: Ï€1 = Ï€2 and Hα : Ï€1 > Ï€2, show that the P-value equals 1/64 for the exact unconditional test and 1/20 for Fisher€™s exact test.
P(X > 6) = E P(X > 6 +1 = k)P(n+ = k) . k=0 - 0.10 (8)(1/2)*), %3D 32
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The observed table has X 2 6 The probabi... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


