Question: Repeat Example 20-4 but using repressurization with pure product. A 0.50 m long column is used to remove methane (M) from hydrogen using Calgon Carbon
Repeat Example 20-4 but using repressurization with pure product.
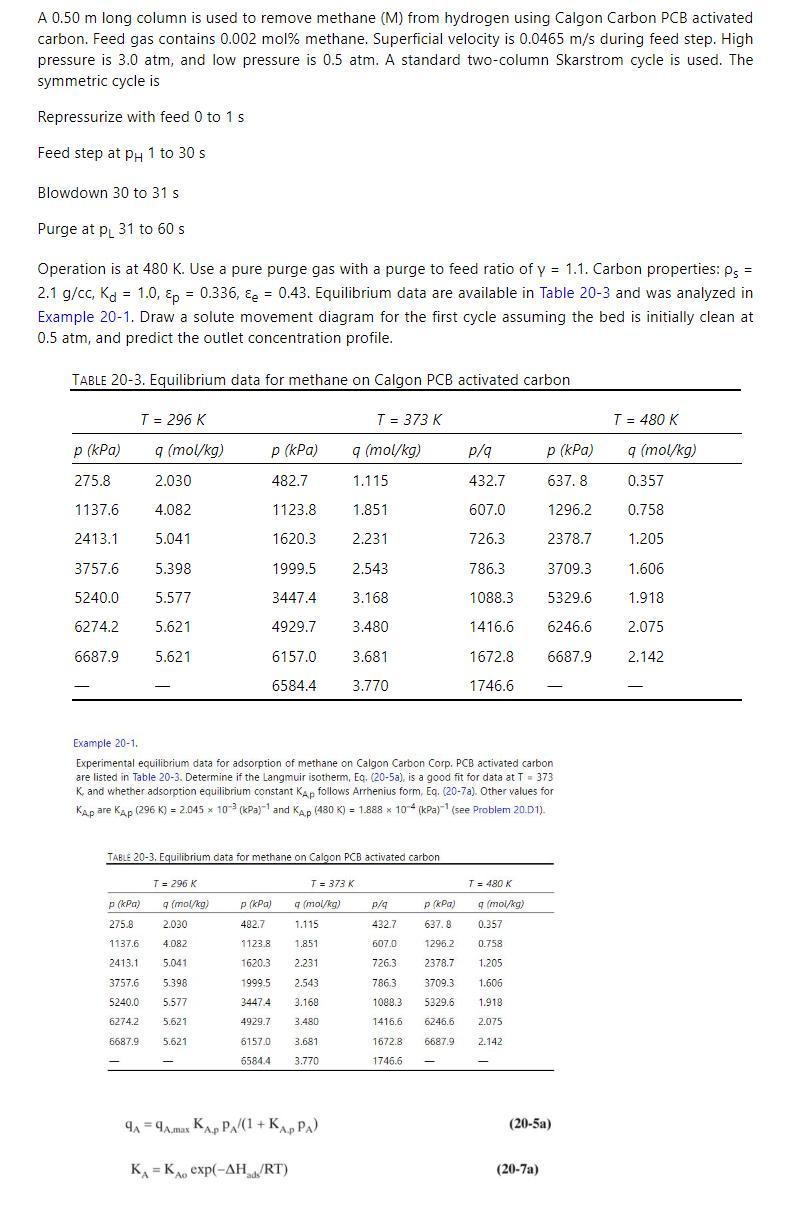
A 0.50 m long column is used to remove methane (M) from hydrogen using Calgon Carbon PCB activated carbon. Feed gas contains 0.002 mol% methane. Superficial velocity is 0.0465 m/s during feed step. High pressure is 3.0 atm, and low pressure is 0.5 atm. A standard two-column Skarstrom cycle is used. The symmetric cycle is Repressurize with feed 0 to 1 s Feed step at pH 1 to 30 s Blowdown 30 to 31 s Purge at p 31 to 60 s = Operation is at 480 K. Use a pure purge gas with a purge to feed ratio of y = 1.1. Carbon properties: P 2.1 g/cc, Kd 1.0, p = 0.336, &e = 0.43. Equilibrium data are available in Table 20-3 and was analyzed in Example 20-1. Draw a solute movement diagram for the first cycle assuming the bed is initially clean at 0.5 atm, and predict the outlet concentration profile. TABLE 20-3. Equilibrium data for methane on Calgon PCB activated carbon T = 296 K T = 373 K T = 480 K p (kPa) q (mol/kg) p (kPa) q (mol/kg) p/q p (kPa) q (mol/kg) 275.8 2.030 482.7 1.115 432.7 637.8 0.357 1137.6 4.082 1123.8 1.851 607.0 1296.2 0.758 2413.1 5.041 1620.3 2.231 726.3 2378.7 1.205 3757.6 5.398 1999.5 2.543 786.3 3709.3 1.606 5240.0 5.577 3447.4 3.168 1088.3 5329.6 1.918 6274.2 5.621 4929.7 3.480 1416.6 6246.6 2.075 6687.9 5.621 6157.0 3.681 1672.8 6687.9 2.142 6584.4 3.770 1746.6 Example 20-1. Experimental equilibrium data for adsorption of methane on Calgon Carbon Corp. PCB activated carbon are listed in Table 20-3. Determine if the Langmuir isotherm, Eq. (20-5a), is a good fit for data at T = 373 K, and whether adsorption equilibrium constant Kap follows Arrhenius form, Eq. (20-7a). Other values for KAP are Kp (296 K) = 2.045 x 103 (kPa) and Kap (480 K) = 1.888 x 104 (kPa) (see Problem 20.D1). TABLE 20-3, Equilibrium data for methane on Calgon PCB activated carbon T = 296 K T = 373 K T = 480 K p (kPa) 275.8 q (mol/kg) 2.030 P (kPa) 482.7 q (mol/kg) 1.115 p/q 432.7 P (kPa) q (mol/kg) 1137.6 4.082 1123.8 1.851 607.0 637.8 1296.2 0.357 0.758 2413.1 5.041 1620.3 2.231 726.3 2378.7 1.205 3757.6 5.398 5240.0 5.577 6274.2 6687.9 5.621 5.621 1999.5 2.543 3447.4 3.168 4929.7 3.480 6157.0 6584.41 3.770 786.3 3709.3 1.606 1088.3 5329.6 1.918 3.681 1416.6 6246.6 1672.8 1746.6 2.075 6687.9 2.142 9A9A.max KA PA/(1+ KAPPA) KA KA exp(-AHRT) (20-5a) (20-7a)
Step by Step Solution
3.28 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


