Question: Spherical particles are used in many practical applications including adsorption and ion exchange. Mass transfer in such particles can be described starting with a differential
Spherical particles are used in many practical applications including adsorption and ion exchange. Mass transfer in such particles can be described starting with a differential material balance in spherical coordinates. If the intraparticle diffusivity is constant, starting with an initially uniform concentration ![]() and with a uniform surface concentration
and with a uniform surface concentration ![]() , the average concentration in the particle
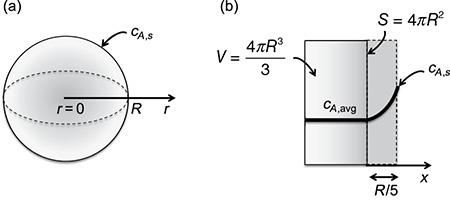
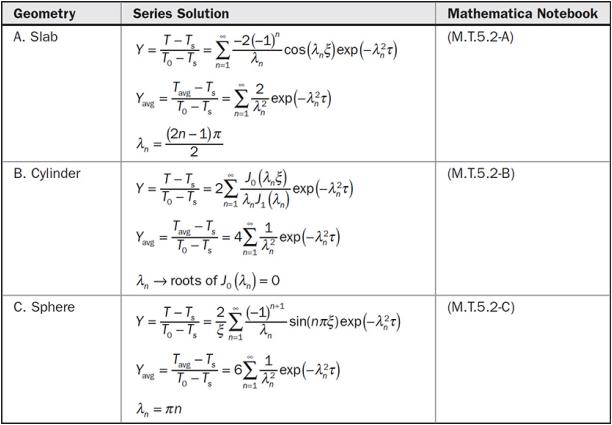
, the average concentration in the particle ![]() is given in dimensionless form by item C in Table 5.2. With reference to Fig.P.15.4, an approximate solution of this mass transfer problem can be found using a pseudo-steady-state approximation by assuming that the mass transfer resistance in the sphere is represented by diffusion through a solid film with thickness
is given in dimensionless form by item C in Table 5.2. With reference to Fig.P.15.4, an approximate solution of this mass transfer problem can be found using a pseudo-steady-state approximation by assuming that the mass transfer resistance in the sphere is represented by diffusion through a solid film with thickness ![]() where R is the actual particle radius. With a constant diffusivity,
where R is the actual particle radius. With a constant diffusivity, ![]() , the diffusion flux of A across this film is:
, the diffusion flux of A across this film is:
FIGURE P.15.4:
![]()
Assuming pseudo-steady-state, ![]() is constant across the film. Thus,integrating this equation across the film we obtain:
is constant across the film. Thus,integrating this equation across the film we obtain:
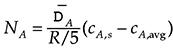
A material balance yields the following equation:
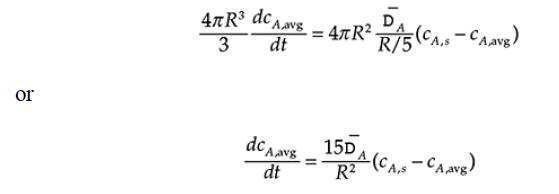
Separating the variables and integrating gives:
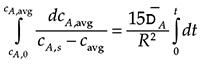
The final result is:
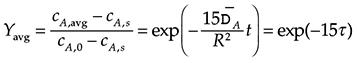
where ![]() . Although this expression is only approximate, thissimplified approach has the advantage that it can be easily extended to cases where the diffusivity is composition dependence. In the adsorption field, this is called the linear driving force approximation (LDF) and is used extensively in lieu of the more complex description of transport in spherical coordinates.
. Although this expression is only approximate, thissimplified approach has the advantage that it can be easily extended to cases where the diffusivity is composition dependence. In the adsorption field, this is called the linear driving force approximation (LDF) and is used extensively in lieu of the more complex description of transport in spherical coordinates.
(a) Compare the result of the film model approximation above for the case of constant ![]() with the exact solution by item C in Table 5.2 by plotting
with the exact solution by item C in Table 5.2 by plotting ![]() vs.
vs. ![]() in both cases.
in both cases.
(b) Extend the film model approximation analysis to the ion exchange of two ions A and B with diffusivities ![]() and
and ![]() assuming
assuming ![]() and
and ![]() . In this case, the flux is given by:
. In this case, the flux is given by:
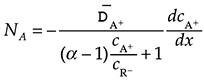
(c) Compare the results of your extension with the exact solution for diffusion in a spherical ion-exchange particle (Eq. (15.61)) by plotting ![]() vs.
vs. ![]() in the two cases for
in the two cases for ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
TABLE 5.2:
A,0
Step by Step Solution
3.33 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


