Confirm that the results of the example Example 8.7 do conserve momentum in both the x- and
Question:
Confirm that the results of the example Example 8.7 do conserve momentum in both the x- and y-directions.
Data given in Example 8.7
Suppose the following experiment is performed. A 0.250-kg object (m1) is slid on a frictionless surface into a dark room, where it strikes an initially stationary object with mass of 0.400 kg (m2) . The 0.250-kg object emerges from the room at an angle of 45.0° with its incoming direction. The speed of the 0.250-kg object is originally 2.00 m/s and is 1.50 m/s after the collision. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the velocity (v'2 and θ2) of the 0.400-kg object after the collision.
Strategy
Momentum is conserved because the surface is frictionless. The coordinate system shown in Figure 8.11 is one in which m2 is originally at rest and the initial velocity is parallel to the -axis, so that conservation of momentum along the x- and y-axes is applicable.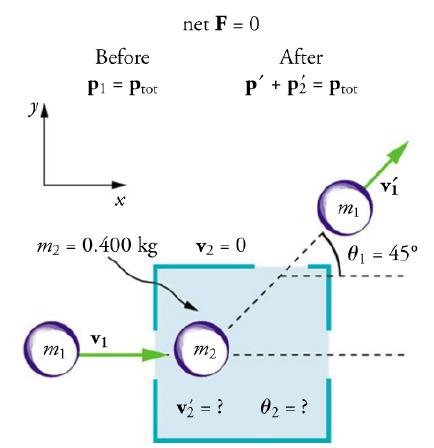
Step by Step Answer:






