Table 13.5 gives the vapor pressure of water at 20.0C as 2.33 x 10 3 Pa. Use
Question:
Table 13.5 gives the vapor pressure of water at 20.0°C as 2.33 x 103 Pa. Use the ideal gas law to calculate the density of water vapor in g/m3 that would create a partial pressure equal to this vapor pressure. Compare the result with the saturation vapor density given in the table.
Strategy
To solve this problem, we need to break it down into a two steps. The partial pressure follows the ideal gas law,

where n is the number of moles. If we solve this equation for n/V to calculate the number of moles per cubic meter, we can then convert this quantity to grams per cubic meter as requested. To do this, we need to use the molecular mass of water, which is given in the periodic table.
Data given in Table 13.5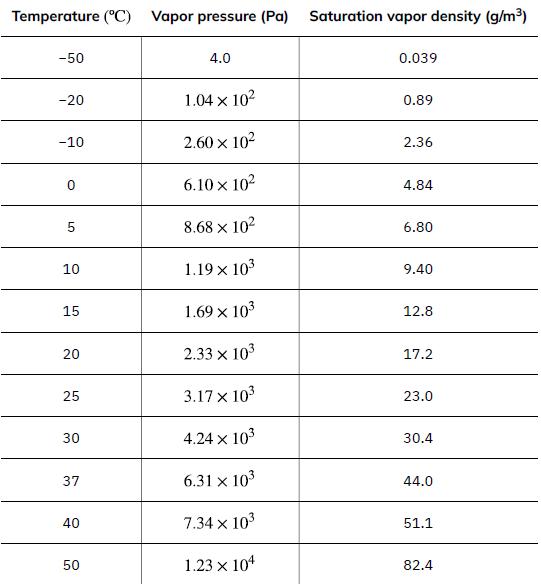
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





