Question: Keplers second law, the statement that a planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times, can be derived by a geometrical argument. To see how
Figure Q5.6
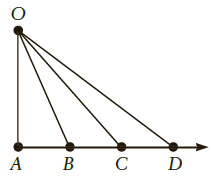
A B C D
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The area of a triangle is one half the base times the h... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


