Question: Repeat 4.23.1 for the always-not-taken predictor. Exercise 4.23.1 Stall cycles due to mispredicted branches increase the CPI. What is the extra CPI due to mispredicted
Repeat 4.23.1 for the “always-not-taken” predictor.
Exercise 4.23.1
Stall cycles due to mispredicted branches increase the CPI. What is the extra CPI due to mispredicted branches with the always-taken predictor? Assume that branch outcomes are determined in the EX stage, that there are no data hazards, and that no delay slots are used.
The importance of having a good branch predictor depends on how often conditional branches are executed. Together with branch predictor accuracy, this will determine how much time is spent stalling due to mispredicted branches. In this exercise, assume that the breakdown of dynamic instructions into various instruction categories is as follows: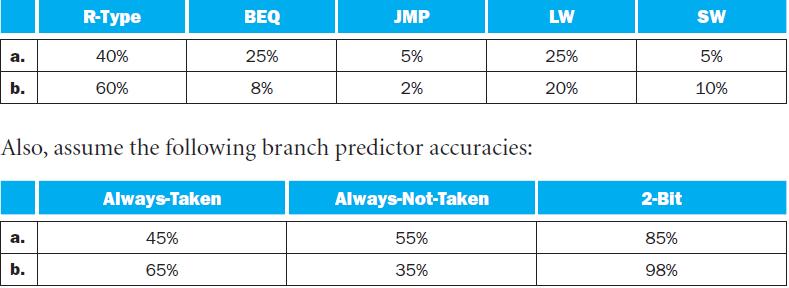
a. b. a. R-Type b. 40% 60% BEQ 45% 65% 25% 8% Also, assume the following branch predictor accuracies: Always-Taken JMP 5% 2% Always-Not-Taken 55% 35% LW 25% 20% 2-Bit 85% 98% SW 5% 10%
Step by Step Solution
3.30 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To calculate the extra CPI Cycles Per Instruction due to mispredicted branches with the alwaysnottak... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


