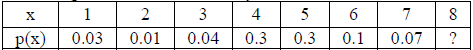
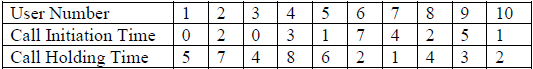
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


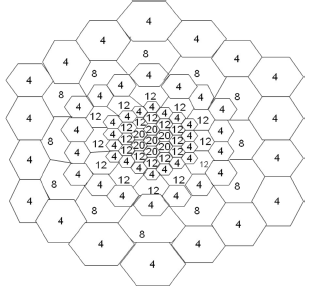
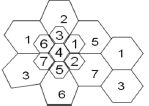
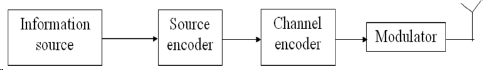
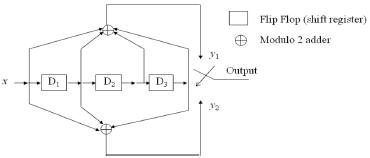
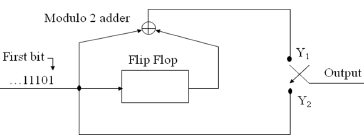
![100 0 1 1 0] 0 10 0 0 1 1 G = 0 0 10 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 10 1](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/6/0/3/9505fd216ee17dfd1607603949653.jpg)