Question: Examine the genetic code in Table 16.1. Are point mutations in the first, second, and third positions of a codon equally likely to cause a
Examine the genetic code in Table 16.1. Are point mutations in the first, second, and third positions of a codon equally likely to cause a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein? What type of point mutation is least likely to change the amino acid sequence?
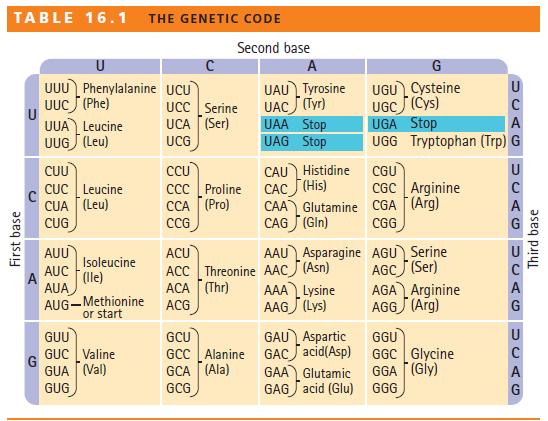
First base TABLE 16.1 THE GENETIC CODE Second base U A G UUU Phenylalanine UCU UAU Tyrosine UUC (Phe) U UCC Serine UAC (Tyr) UGU Cysteine UGC (Cys) U UUA Leucine UCA (Ser) UAA Stop UGA Stop A UUG (Leu) UCG UAG Stop UGG Tryptophan (Trp) G CUU CCU CUC Leucine CCC Proline CAU Histidine CAC (His) CGU U CGC Arginine CUA (Leu) CUG AUU AUC CCA (Pro) CCG CAG (Gin) ACU CAA Glutamine CGA (Arg) AAU Asparagine AGU Serine A CGG Isoleucine (Ile) ACC Threonine AAC (Asn) AGC (Ser) AUA ACA (Thr) AAA Lysine AGA Arginine AUG-Methionine ACG or start AAG (Lys) AGG (Arg) G GUU GCU GAU Aspartic GGU U GUC Valine GCC Alanine GAC acid(Asp) GGC Glycine C GUA (Val) GCA (Ala) GAA Glutamic GGA (Gly) A GUG GCG GAG acid (Glu) GGG G Third base
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


