Question: Consider the cantilever beam problem shown previously in Exercise 8.2 with no axial force (N =0). Assume a plane stress anisotropic model given by Hookes
Consider the cantilever beam problem shown previously in Exercise 8.2 with no axial force (N =0). Assume a plane stress anisotropic model given by Hooke’s law (11.5.1) and governed by the Airy stress function equation (11.5.6). Show that the stress function:
![3P [cxy- 4c3 xy S16 -+ 3 6511 - (26x - y)] 3P 0x = -2-3x - 2018 (G-2). ox xy+ 3P S16 2c3 S113 satisfies the](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/1/2/6/36765a229df7c50a1705126366841.jpg)
Next show that these stresses satisfy the problem boundary conditions in the usual sense with
exact pointwise specification on y =± c, and only resultant force conditions on the end's x = 0
and x = L. What happens to this solution if we let the material become orthotropic?
Data from exercise 8.2
Show that the Airy function:
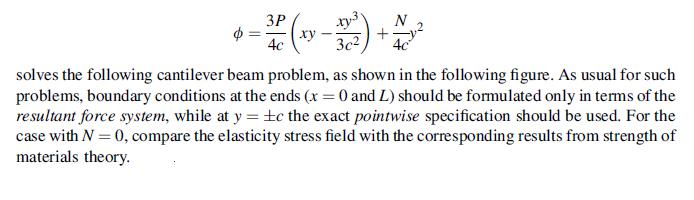
Equation 11.5.1
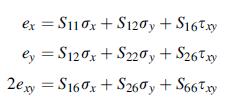
Equation 11.5.6
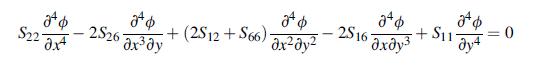
3P [cxy- 4c3 xy S16 -+ 3 6511 - (26x - y)] satisfies the governing equation and gives the following stress field oy = 0 ty--3 (1-2) = 3P 4c 3P 0x = -2-3x - 2018 (G-2). ox xy+ 3P S16 2c3 S113
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
3P 4c 00 3P CELL 2 atu S2 2526 ax 0 For planestress ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


