Question: For Example, 10.3 with = 0, verify that the stresses from equation (10.5.18) reduce to those previously given in Eq. (8.4.69). Data from example
For Example, 10.3 with α = 0, verify that the stresses from equation (10.5.18) reduce to those previously given in Eq. (8.4.69).
Data from example 10.3
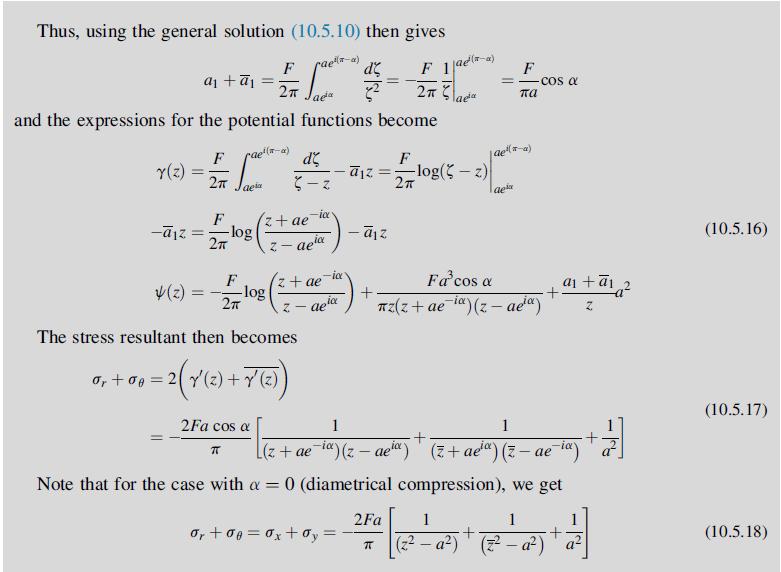
Equation 10.5.18
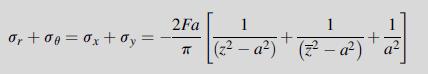
Equation 8.4.69
![0x Txy = 2P [(R-y)x 1 2P (R - y) 3 2P [(R-y)-x (R+y)x2 (R+y) 3. 4 (R+y)?x] D](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/0/6/1/97965a12e5b4ee241705061979239.jpg)
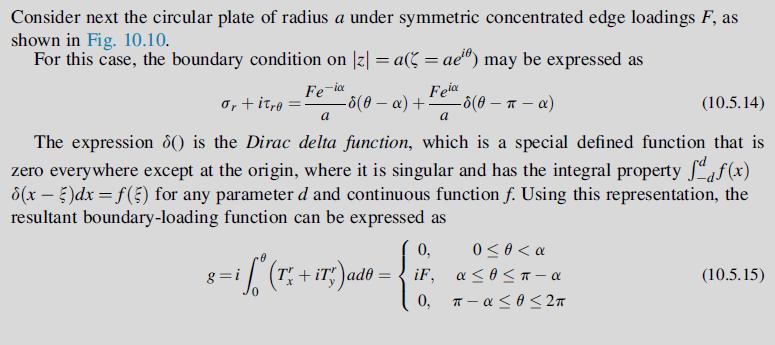
Consider next the circular plate of radius a under symmetric concentrated edge loadings F, as shown in Fig. 10.10. For this case, the boundary condition on |z| = a( = ae) may be expressed as -ia Fe Feia -8(0-) +- -5 (0- - ) a or +itre (10.5.14) a The expression 8() is the Dirac delta function, which is a special defined function that is zero everywhere except at the origin, where it is singular and has the integral property f(x) 8(x - 5)dx = f(5) for any parameter d and continuous function f. Using this representation, the resultant boundary-loading function can be expressed as 0, g=i = i [ ^ (r + iT;) ado = . { / iF, 0, 0 0
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
From 10518 0 0 0 0 2P 2F ax From 8469 for loading along t... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


