As described in the chapter, the abnormal earnings approach for estimating common share value is where V
Question:
As described in the chapter, the abnormal earnings approach for estimating common share value is
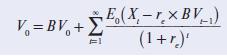
where V0 is the total value of all outstanding shares, BV0 is the current book value of stockholders’ equity, BVt–1 is the book value of shareholders’ equity at the beginning of period t, re is the cost of equity capital, E0 is the expectations operator, and Xt is period t net income. The model says that share value equals the book value of stockholders’ equity plus the present value of future expected abnormal earnings (where abnormal earnings is net income minus the cost of equity capital multiplied by the beginning-of period book value of stockholders’ equity).
The model is silent on how one comes up with expected net income for future years (and therefore future expected abnormal earnings) and just how many future years should be used.
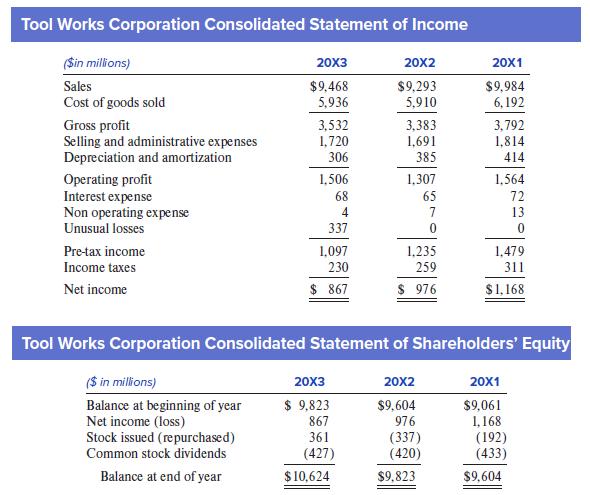
Because of the way present value is calculated, abnormal earnings amounts expected for years in the distant future have a small present value and are essentially irrelevant to valuation, especially if abnormal earnings are close to zero in the long run, as many analysts assume. Thus, professional analysts rarely use more than 15 years, often fewer than 10. Comparative income statements and statements of shareholders’ equity for Tool Works Corporation for 20X1–20X3 follow.
Required:
1. Assume a 10-year forecasting horizon. Note that 20X3 return on beginning stockholders’ equity (net income divided by beginning 20X3 stockholders’ equity), adjusted to exclude unusual items and their tax effects, is 11.5%. (If we add $337 × [1 – 0.21] = $266 back to net income, we get $867 + $266 = $1,133 of adjusted net income. Dividing that amount by $9,823 gives 11.5%.) Assume return on beginning stockholders’ equity will persist at 11.5% throughout the forecasting horizon, with no additional unusual items. That is, expected net income is always equal to 0.115 multiplied by beginning-of-the-year stockholders’ equity. Also assume that no additional stock issuances or repurchases are made and that dividends equal 40% of net income in each year. (This is the approximate historical dividend payout ratio.) Finally assume that the cost of equity capital is 9%. With these relatively simple assumptions, use the abnormal earnings model to estimate the total value of common shares as of the end of 20X3. Ignore terminal values at the end of the 10-year forecast horizon in your calculations.
2. As of the end of 20X3, 307 million common shares were outstanding. Convert your estimate in requirement 1 to a per share estimate. Do you expect that the actual market price would be similar to, above, or below the value you estimated?
3. Now assume the company will maintain a 16% return on beginning stockholders’ equity over the 10-year forecast horizon. What would the company’s shares then be worth?
Step by Step Answer:

Financial Reporting And Analysis
ISBN: 9781260247848
8th Edition
Authors: Lawrence Revsine, Daniel Collins, Bruce Johnson, Fred Mittelstaedt, Leonard Soffer





