Tesco plc is one of the worlds largest food retailers. Fiscal year 2014 (the year ended February
Question:
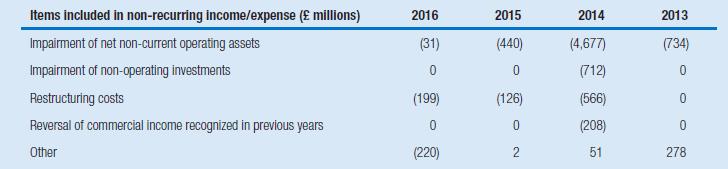
Tesco plc is one of the world’s largest food retailers. Fiscal year 2014 (the year ended February 28, 2015) was a rocky year for the retailer. The company’s sales and margins had come under pressure as a result of strong competition in the industry. Further, in September 2014 company management announced that it had overstated earnings in previous fiscal years through the accelerated recognition of supplier rebates. The events led to a management change in which Dave Lewis took over as chief executive and John Allen took over as chairman. In April 2015 Dave Lewis announced a record (pre-tax) loss of £6.4 billion – one of the largest losses in UK history. This loss was attributable, at least in part, to a £4.7 billion impairment of property, plant, and equipment, a £0.7 billion impairment of (non-operating) investment assets, and a restructuring charge of £0.6 billion.
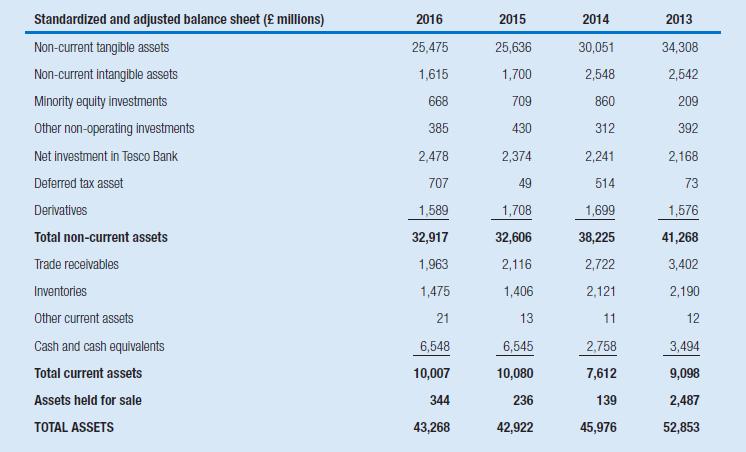
The following tables show the standardized and adjusted income statements and balance sheets of Tesco, for the years ended February 28, 2014, 2015, 2016, and 2017. Operating lease obligations have been capitalized, and the operating lease expense has been replaced with depreciation and interest expense, following the procedure described in Chapter 4.
Further, to help you better analyze the retail activities of Tesco, the net assets of Tesco Bank have been included as one separate balance sheet item, labelled “Net investment in Tesco Bank”; Tesco Bank’s pre-tax profit is separately reported in the income statement.
Tesco’s statutory tax rate was 23.1 percent in 2013, 21.2 percent in 2014, 20.1 percent in 2015, and 20.0 percent in 2016.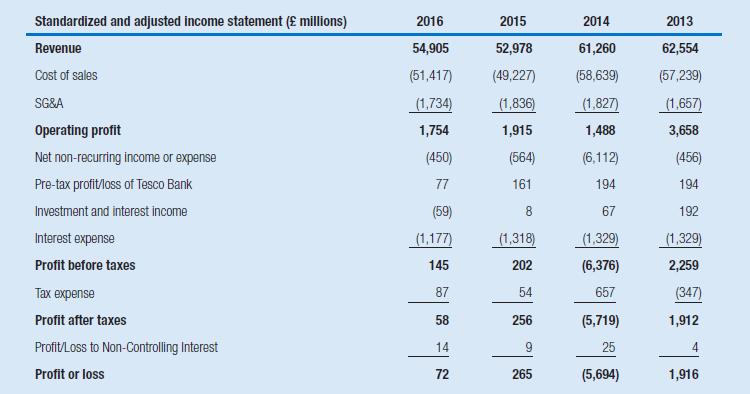
1 Calculate Tesco’s net operating profit after tax, net investment profit after tax, interest after tax, operating working capital, net non-current operating assets, non-operating investments, business assets, debt, and capital for the years 2013–2016.
2 Decompose Tesco’s return on equity for the years 2013–2016 using the traditional approach.
3 Decompose Tesco’s return on equity for the years 2013–2016 using the alternative approach. What explains the difference between Tesco’s return on assets and its return on net operating assets?
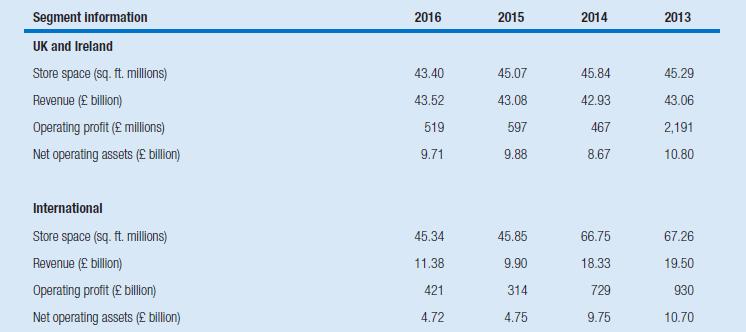
4 Analyze the underlying drivers of the change in Tesco’s return on equity, also making use of the non-financial statistics and segment information.
Which factors explain the decrease in return on equity in 2014? To what extent can you conclude that Tesco’s transformation plan is effective in 2015 and 2016?
Step by Step Answer:

Business Analysis And Valuation
ISBN: 978-1473758421
5th Edition
Authors: Erik Peek, Paul Healy, Krishna Palepu





