Question: Example 4 dealt with the case 4h > kM 2 in the equation dx/dt = kx (M - x) - h that describes constant-rate harvesting
Example 4 dealt with the case 4h > kM2 in the equation dx/dt = kx (M - x) - h that describes constant-rate harvesting of a logistic population. Problems 26 and 27 deal with the other cases.
If 4h > kM2, show that x(t) = 0 after a finite period of time, so the lake is fished out (whatever the initial population). Then solve explicitly by separation of variables.] The results of this and the previous problem (together with Example 4) show that h = 1/4 kM2 is a critical harvesting rate for a logistic population. At any lesser harvesting rate the population approaches a limiting population N that is less than M (why?), whereas at any greater harvesting rate the population reaches extinction.
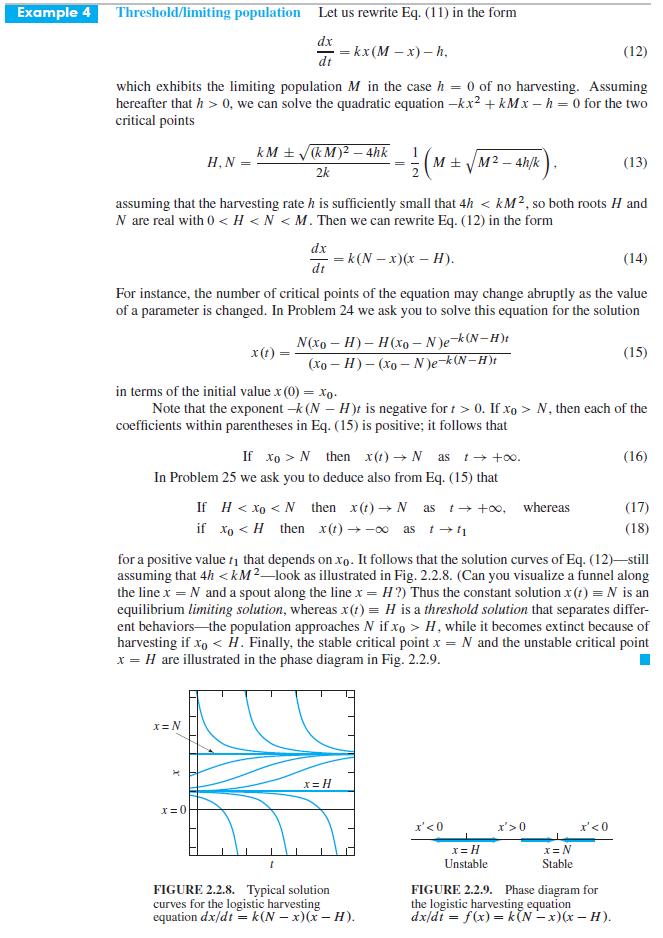
Example 4 Threshold/limiting population (12) = which exhibits the limiting population M in the case h 0 of no harvesting. Assuming hereafter that h> 0, we can solve the quadratic equation -kx +kMx-h=0 for the two critical points H, N Let us rewrite Eq. (11) in the form dx dt kM (KM) - 4hk 2k x=N = kx (M-x) - h. x=0 assuming that the harvesting rate h is sufficiently small that 4h < KM2, so both roots H and N are real with 0 N, then each of the coefficients within parentheses in Eq. (15) is positive; it follows that If H < xo < N then x(t) N as t +o, whereas if xo 0 x = N Stable x'
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Separation of variables in th... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


