Question: Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, two- dimensional velocity field of Prob. 417. The pressure field is given by where P 0 is
Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, two- dimensional velocity field of Prob. 4–17. The pressure field is given by
![P = Po -[20,x+ 2U bx + b(x + y) - 1-)]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1694/5/0/5/283650019431acfd1694505282716.jpg)
where P0 is the pressure at x = 0. Generate an expression for the rate of change of pressure following a fluid particle.
Data from Problem 17
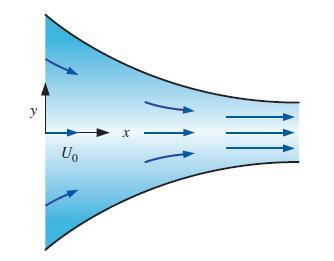
Consider steady, incompressible, two-dimensional flow through a converging duct (Fig. P4–17). A simple approximate velocity field for this flow is
![]()
where U0 is the horizontal speed at x = 0. Note that this equation ignores viscous effects along the walls but is a reasonable approximation throughout the majority of the flow field. Calculate the material acceleration for fluid particles passing through this duct. Give your answer in two ways:
(1) As acceleration components ax and ay
(2) As acceleration vector a(vector)
P = Po -[20,x+ 2U bx + b(x + y) - 1-)]
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


