Consider the same situation as in problem 13.31, but in this case one membrane provides a constant
Question:
Consider the same situation as in problem 13.31, but in this case one membrane provides a constant flux into the fluid while the other provides a flux of the same magnitude out of the fluid. What is the Sherwood number for each surface and how does that compare to the annulus case (problem 13.27)?
Problem 13.27
Consider fully developed flow inside the annulus shown in Figure P13.27. Both velocity and temperature profiles are fully developed. The heat fluxes in from the two walls are different but are constant along the length of the annulus.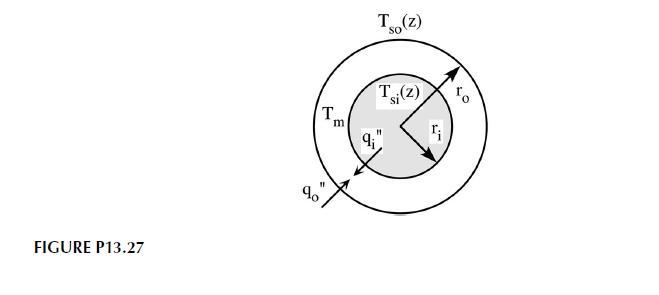
Problem 13.31
We are interested in determining the Sherwood number in fully developed flow between parallel plates. The plates are formed from membranes that provide a constant mass flux into the fluid along their length as shown in Figure P13.31. Derive the differential equation describing this situation and determine the Sherwood number. How does the Sherwood number compare with the corresponding case for flow in a tube?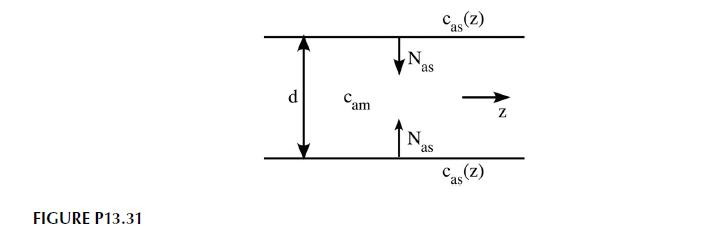
Step by Step Answer:






