For medical uses, radon-222 formed in the radioactive decay of radium-226 is allowed to collect over the
Question:
For medical uses, radon-222 formed in the radioactive decay of radium-226 is allowed to collect over the radium metal. Then, the gas is withdrawn and sealed into a glass vial. Following this, the radium is allowed to disintegrate for another period, when a new sample of radon-222 can be withdrawn. The procedure can be continued indefinitely. The process is somewhat complicated by the fact that radon-222 itself undergoes radioactive decay to polonium-218, and so on. The half-lives of radium-226 and radon-222 are 1.60 x 103 years and 3.82 days, respectively.
(a) Beginning with pure radium-226, the number of radon-222 atoms present starts at zero, increases for a time, and then falls off again. Explain this behavior. That is, because the half-life of radon-222 is so much shorter than that of radium-226, why doesn’t the radon-222 simply decay as fast as it is produced, without ever building up to a maximum concentration?
(b) Write an expression for the rate of change (dD/dt) in the number of atoms (D) of the radon-222 daughter in terms of the number of radium-226 atoms present initially (N0) and the decay constants of the parent (λp) and daughter (λd).
(c) Integration of the expression obtained in part (b) yields the following expression for the number of atoms of the radon-222 daughter (D) present at a time t.
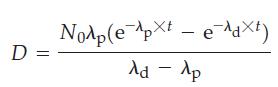
Starting with 1.00 g of pure radium-226, approximately how long will it take for the amount of radon-222 to reach its maximum value: one day, one week, one year, one century, or one millennium?
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





