Question: Additional data needed for this question can be found in Appendix 11. (a) Determine E Zn 2+ /Zn (at 298 K) for a half-cell in
Additional data needed for this question can be found in Appendix 11.
(a) Determine EZn2+/Zn (at 298 K) for a half-cell in which [Zn2+] = 0.25 mol dm−3.
(b) Calculate the reduction potential for the half reaction:
![]()
if the ratio of the concentrations of [VO]2+: V3+ is 1 :2 and the pH of the solution is 2.2.
Data from Appendix 11
The concentration of each aqueous solution is 1 mol dm−3 and the pressure of a gaseous component is 1 bar (105 Pa). (Changing the standard pressure to 1 atm (101 300 Pa) makes no difference to the values of Eo at this level of accuracy.) Each half-cell listed contains the specified solution species at a concentration of 1 mol dm−3; where the half-cell contains [OH]−, the value of Eo refers to [OH−] = 1 mol dm−3, hence the notation Eo[OH−] = 1
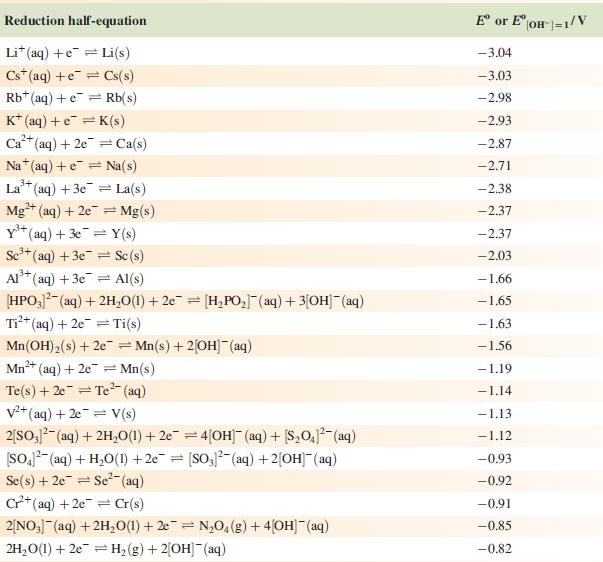

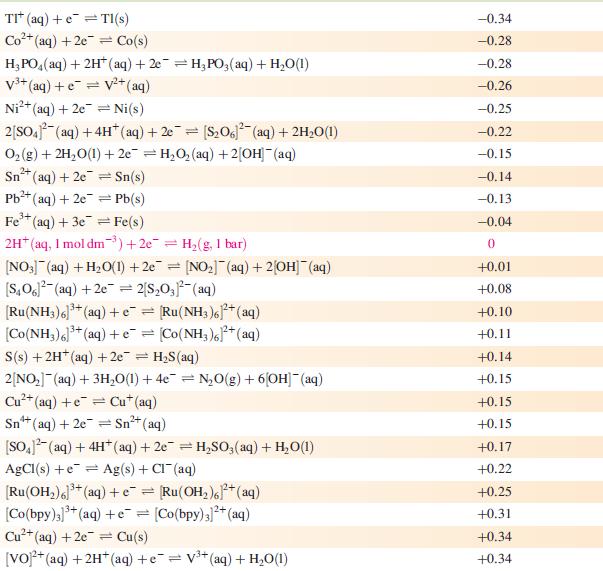
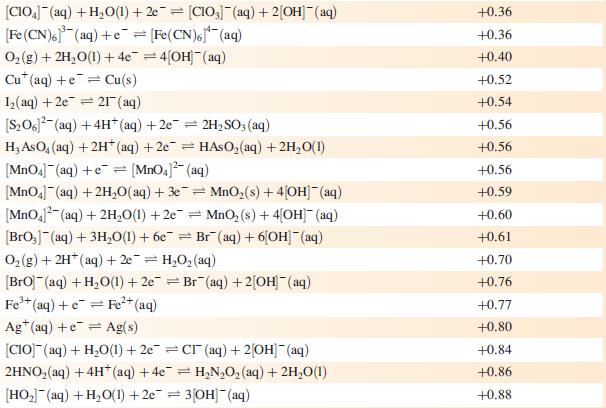
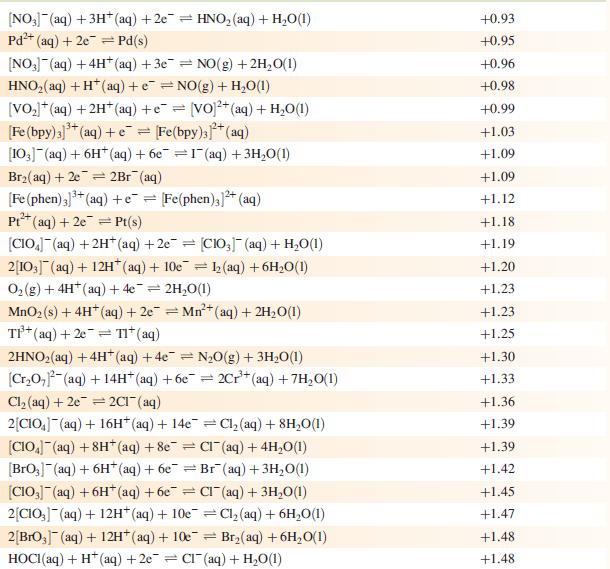

[VO]+ (aq) + 2H+ (aq) +e=V+ (aq) + HO(1)
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (146 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To solve this question we will use the Nernst equation which relates the reduction potential E of an electrochemical cell at nonstandard conditions to ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


