A distillation column with a total condenser is shown in Fig. 3.3. The system to be studied
Question:
A distillation column with a total condenser is shown in Fig. 3.3. The system to be studied in this problem has an average enthalpy of vaporization of 32 kJ/mol, an average CPL of 146 J/mol°-C, and an average CPV of 93 J/mol°-C. Variable names for the various stream flow rates and the heat flow rates are given in the diagram. The feed can be liquid, vapor, or a mixture represented using subscripts to indicate the vapor and liquid flows, F = FV + FL. The enthalpy flow due to feed can be represented as: for saturated liquid, FLHsatL; for saturated vapor, FVHsatV; for subcooled liquid, FLHsatL + FLCPL (TF – TsatL); for superheated vapor, FVHsatV + FVCPV(TF – TsatV); and for a mix of vapor and liquid, FLHsatL + FV HsatV.
(a) Use a mass balance to show FV + VS – VR = LS – LR – FL.
[For parts (b) - f), use the feed section mass and energy balances to show the desired result.]
(b) For saturated vapor feed, FL = 0. Show VR = VS + FV , LS = LR.
(c) For saturated liquid feed, FV = 0. Show VS = VR, LS = LR + FL.
(d) For subcooled liquid feed, FV = 0. Show VR – VS = FLCP(TF – Tsat)/ΔHvap.
(e) For superheated vapor feed, FL = 0, Show LS – LR = –FVCP(TF – Tsat)/ΔHvap.
(f) For a feed mixture of saturated liquid and saturated vapor. Show VR = VS + FV, LS = LR + FL.
(g) Use the mass and energy balances around the total condenser to relate the condenser duty to the enthalpy of vaporization, for the case of streams LR and D being saturated
liquid.
(h) Use the mass and energy balances around the reboiler to relate the reboiler duty to the enthalpy of vaporization.
(i) In the case of subcooled liquid streams LR and D, the vapor flows out of the top of the column, and more variables are required. V′R (into the condenser) will be smaller than the rectifying section flow rate VR. Also, the liquid flow rate in the rectifying section, Also, the liquid flow rate in the rectifying section, LR, will be larger than the reflux back to the column, L′R. Using the variables V′R, L′R to represent the flow rate out of the top of the column and the reflux, respectively, relate VR to V′R L′R and the degree of subcooling TL – TsatL.
[For parts (j) - (o), find all other flow rates and heat exchanger duties ( values).]
(j) F = 100 mol/hr (saturated vapor), B = 43, LR/D = 2.23.
(k) F = 100 mol/hr (saturated vapor), D = 48, LS/VS = 2.5.
(l) F = 100 mol/hr (saturated liquid), D = 53, LR/D = 2.5.
(m) F = 100 mol/hr (half vapor, half liquid), B = 45, LS/VS = 1.5.
(n) F = 100 mol/hr (60°C subcooled liquid), D = 53, LR/D = 2.5.
(o) F = 100 mol/hr (60°C superheated vapor), D = 48, LS/VS = 1.5.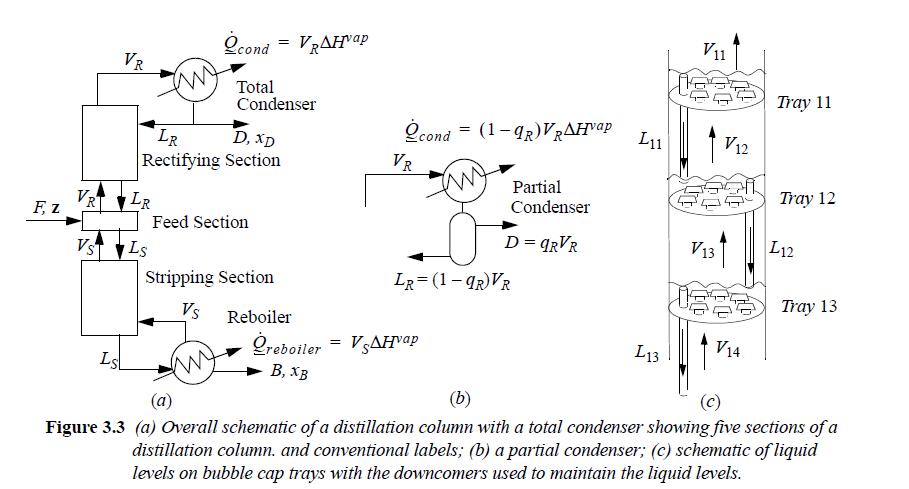
Step by Step Answer:

Introductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9780136068549
2nd Edition
Authors: J. Elliott, Carl Lira





