Question: Generalizing the Chevalier de Mr problem (see Exercise 16 in Section 2.3), suppose pk denotes the probability that we get at least one six when
Generalizing the Chevalier de Méré problem (see Exercise 16 in Section 2.3), suppose pk denotes the probability that we get at least one six when we throw a die k times, and qk denotes the probability that we get at least one double six when we throw two dice 6k times.
(i) Verify that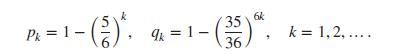
(ii) Use a series of commands similar to those given in the previous exercise
(a) to draw plots of pk and qk for different values of k,
(b) to find the smallest value of k such that pk is at least I. 50% II. 90%
III. 95%.
Find also for which values of k the probability qk exceeds each of these three values above.
(iii) Find the value of k that minimizes the difference between pk and qk.
Pk = 1 - (3)*. 9k = 1- 35 6k 36 k = 1, 2,....
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


