Question: Legendre polynomials. Use the GramSchmidt procedure (Problem A.4) to orthonormalize the functions 1, x,x 2 , and x 3 , on the interval -1
Legendre polynomials. Use the Gram–Schmidt procedure (Problem A.4) to orthonormalize the functions 1, x,x2, and x3, on the interval -1 ≤ x ≤ 1. You may recognize the results—they are (apart from normalization) Legendre polynomials (Problem 2.64 and Table 4.1).
(Problem A.4)

Problem 2.64
Legendre’s differential equation reads
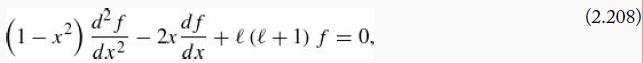
where ℓ is some (non-negative) real number.
orthonormal. Problem A.4 Suppose you start out with a basis (le1), le2),..., len)) that is not The Gram-Schmidt procedure is a systematic ritual for generating from it an orthonormal basis (le), le),..., len)). It goes like this: (i) Normalize the first basis vector (divide by its norm): lei) = le) llei || (ii) Find the projection of the second vector along the first, and subtract it off: le) - (e|e2) lei). This vector is orthogonal tole); normalize it to get le). (iii) Subtract from le3) its projections alongle) and le): les) -(ei e3) |e)-(e|e3)|e). This is orthogonal to le) and le); normalize it to get leg). And so on. Use the Gram-Schmidt procedure to orthonormalize the 3-space basis lei) = (1 + i) + (1) + (i) k, le2) = (i) + (3) + (1) k, le3) = (0) + (28) + (0) k
Step by Step Solution
3.57 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
e 1 eile 1 dr 2 Sole 2 1 e 1 C le 0 x dx 0 ezlez rdr 21 1 GL 12 So Problem A4 es ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


