Consider the data file (m r o z) on working wives. Use the 428 observations on married
Question:
Consider the data file \(m r o z\) on working wives. Use the 428 observations on married women who participate in the labor force. In this exercise, we examine the effectiveness of a parent's college education as an instrumental variable.
a. Create two new variables. MOTHERCOLL is a dummy variable equaling one if MOTHEREDUC \(>12\), zero otherwise. Similarly, FATHERCOLL equals one if FATHEREDUC \(>12\) and zero otherwise. What percentage of parents have some college education in this sample?
b. Find the correlations between EDUC, MOTHERCOLL, and FATHERCOLL. Are the magnitudes of these correlations important? Can you make a logical argument why MOTHERCOLL and FATHERCOLL might be better instruments than MOTHEREDUC and FATHEREDUC?
c. Estimate the wage equation in Example 10.5 using MOTHERCOLL as the instrumental variable. What is the \(95 \%\) interval estimate for the coefficient of \(E D U C\) ?
d. For the problem in part (c), estimate the first-stage equation. What is the value of the \(F\)-test statistic for the hypothesis that MOTHERCOLL has no effect on EDUC? Is MOTHERCOLL a strong instrument?
e. Estimate the wage equation in Example 10.5 using MOTHERCOLL and FATHERCOLL as the instrumental variables. What is the \(95 \%\) interval estimate for the coefficient of \(E D U C\) ? Is it narrower or wider than the one in part (c)?
f. For the problem in part (e), estimate the first-stage equation. Test the joint significance of MOTHERCOLL and FATHERCOLL. Do these instruments seem adequately strong?
g. For the IV estimation in part (e), test the validity of the surplus instrument. What do you conclude?
Data From Example 10.5:-
In addition to education a worker's experience is also important in determining their wage. Because additional years of experience have a declining marginal effect on wage use the quadratic model
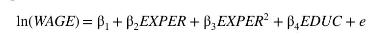
where EXPER is years of experience. This is the same specification. We assume that EXPER is an exogenous variable that is uncorrelated with the worker's ability and therefore uncorrelated with the random error \(e\). Two instrumental variables for years of education, \(E D U C\), are mother's and father's years of education, MOTHEREDUC and FATHEREDUC, introduced in the previous examples. The first-stage equation is
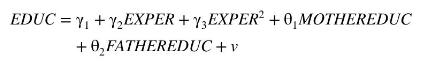
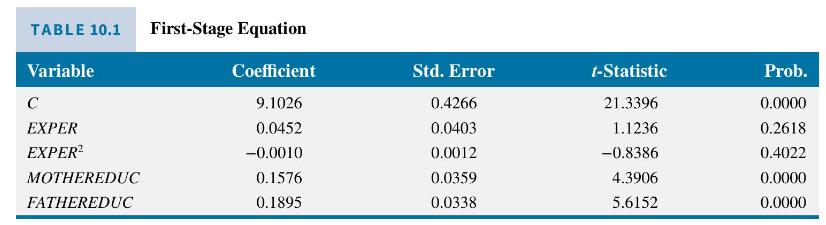
Using the 428 observations in the data file mroz the estimated first-stage equation is reported in Table 10.1. The IV/2SLS estimates, with correctly computed standard errors, are

The estimated return to education is approximately \(6.1 \%\), and the estimated coefficient is statistically significant with a \(t=1.96\).
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Econometrics
ISBN: 9781118452271
5th Edition
Authors: R Carter Hill, William E Griffiths, Guay C Lim





