Question: Consider the potential outcomes framework, where w is a binary treatment indicator and the potential outcomes are y(0) and y(1). Assume that w is randomly
Consider the potential outcomes framework, where w is a binary treatment indicator and the potential outcomes are y(0) and y(1). Assume that w is randomly assigned, so that w is independent of [y(0),y(1)]. Let µ0 = E[y(0)], µ1 = E[y(1)], s20 = Var[y(0)], and s21 = Var[y(1)].
(i) Define the observed outcome as y = (1 – w)y(0) + wy(1). Letting τ = µ1 – µ 0 be the average treatment effect, show you can write
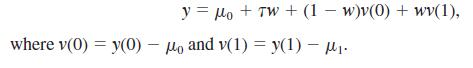
(ii) Let u = (1 – w)v(0) + wv(1) be the error term in
y = µ0 + τw + u
Show that
E(u|w) = 0
What statistical properties does this finding imply about the OLS estimator of t from the simply regression yi on wi for a random sample of size n? What happens as n → ∝?
(iii) Show that
Var(u|w) = E(u2|0w) = (1 – w)s20 + ws21.
Is there generally heteroskedasticity in the error variance?
(iv) If you think s21 ¹ s20, and τ̂ is the OLS estimator, how would you obtain a valid standard error for τ̂?
(v) After obtaining the OLS residuals, ûi, i = 1, . . . , n, propose a regression that allows consistent estimation of s20 and s21.
y = lo + TW + (1 w)v(0) + wv(1), where v(0) = y(0) - Mo and v(1) = y(1) H1.
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (176 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
i First express v in terms of Now plug these values into the equation for y Now use the definition o... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


