Question: The table below provides information for six different bonds: current market price ((P)), the face value of the bond ((V)), and the number of years
The table below provides information for six different bonds: current market price \((P)\), the face value of the bond \((V)\), and the number of years before the bond matures \((N)\).
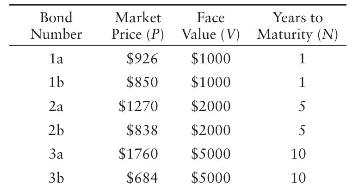
a. In each case, compute the bond's yield, assuming that you buy the bond at its current market price and hold the bond until it matures. There are no coupons. If \(x\) is the bond's yield, then \(P(1+x)^{N}=V\).
b. Suppose bonds 1 a, 2 a, and 3 a are all issued by the same borrower. Can you offer an explanation for the relationship between the bond yields and the terms to maturity?
c. Suppose bonds \(1 \mathrm{~b}, 2 \mathrm{~b}\), and \(3 \mathrm{~b}\) are all issued by the same borrower. What can you conclude about the riskiness of the "a" borrower versus that of the "b" borrower? Explain.
d. Notice that the market interest rate is not shown in the table. Explain why knowledge of the market interest rate is unnecessary in order to compute a bond's yield, once you already know the bond's market price. What aspect of the bond does the market interest rate influence, if anything?
Bond Market Face Years to Number Price (P) Value (V) Maturity (N) 1a $926 $1000 1 1b $850 $1000 1 2a $1270 $2000 5 2b $838 $2000 5 $1760 $5000 10 3b $684 $5000 10
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


