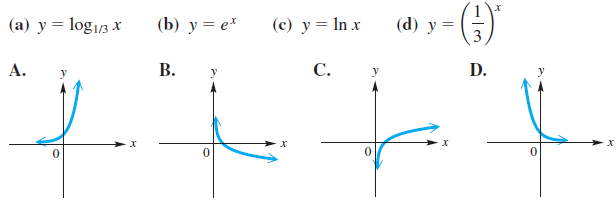
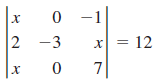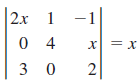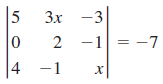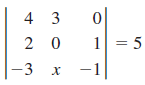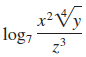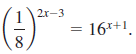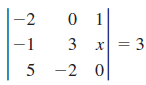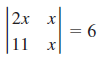![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


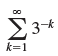
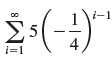
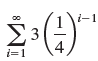
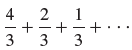
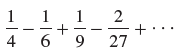
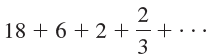
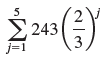
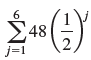
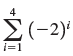
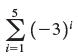
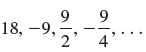
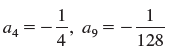
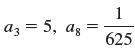
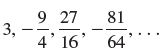
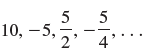
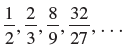
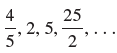
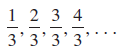
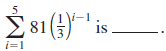

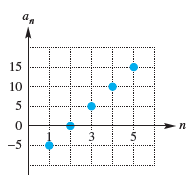
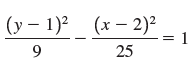
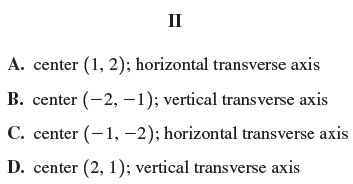
![с сд) аи ан] b11 b12 [b21 b2] C11 C12 [C21 C22 a11 a12 A = [a21 a2. and C= B =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1555/1/4/7/5735cb1ab3584b8b1555130396235.jpg)