Question: In Problem several experiments are simulated using the random number feature on a graphing calculator. For example, the roll of a fair die can be
In Problem several experiments are simulated using the random number feature on a graphing calculator. For example, the roll of a fair die can be simulated by selecting a random integer from 1 to 6, and 50 rolls of a fair die by selecting 50 random integers from 1 to 6. (see Fig. A for Problem and your user’s manual).
From the statistical plot of the outcomes of rolling a fair die 50 times (see Fig. B), we see, for example, that the number 4 was rolled exactly 5 times.
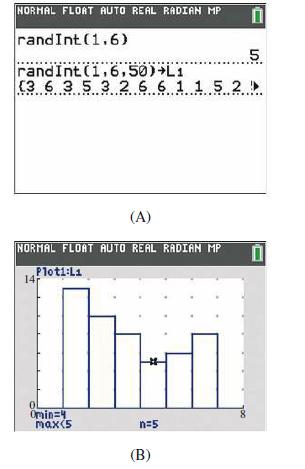
(A) What is the empirical probability that the number 6 was rolled?
(B) What is the probability that a 6 is rolled under the equally likely assumption?
(C) Use a graphing calculator to simulate 100 rolls of a fair die and determine the empirical probabilities of the six outcomes.
NORMAL FLOAT AUTO REAL RADIAN MP rand Int (1.6) 5 randInt (1,6,50) L1 (3 6 3 5 3 2 6 6 1 1 5 2 (A) NORMAL FLOAT AUTO REAL RADIAN MP 14 Ploti:L1 ol Omin=4 max(5 n=5 (B) 8 0
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


