Derive Eqs. (25.98a) for the trace-reversed metric perturbation outside a stationary (time-independent), linearized source of gravity. More
Question:
Derive Eqs. (25.98a) for the trace-reversed metric perturbation outside a stationary (time-independent), linearized source of gravity. More specifically, do the following.
(a) First derive h̅00. In your derivation identify a dipolar term of the form 4Djxj/r3, and show that by placing the origin of coordinates at the center of mass, Eq. (25.96), one causes the dipole moment Dj to vanish.
(b) Next derive h̅0j. The two terms in Eq. (25.97) should give rise to two terms. The first of these is 4Pj/r, where Pj is the source’s linear momentum. Show, using the gauge condition h̅0μ ,μ = 0 [Eq. (25.89)], that if the momentum is nonzero, then the mass dipole term of part (a)must have a nonzero time derivative, which violates our assumption of stationarity. Therefore, the linear momentum must vanish for this source. Show that the second term gives rise to the h̅0j of Eq. (25.98a).
(c) Finally derive h̅ij.
Equations.


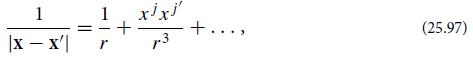
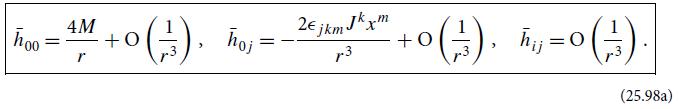
Step by Step Answer:

Modern Classical Physics Optics Fluids Plasmas Elasticity Relativity And Statistical Physics
ISBN: 9780691159027
1st Edition
Authors: Kip S. Thorne, Roger D. Blandford





