Question: Using the method introduced in Question 26, find the solutions of the following initial-value problems: Data from Question 26 Show that by making the substitution
Using the method introduced in Question 26, find the solutions of the following initial-value problems:
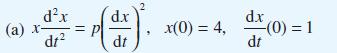
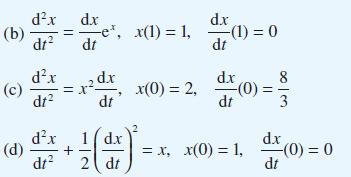
Data from Question 26
Show that by making the substitution
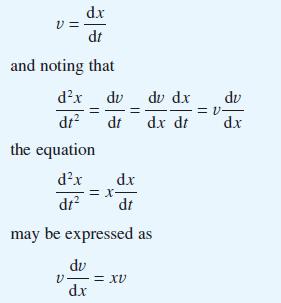
Show that the solution of this equation is v = 1/2x2 + C and hence find x(t). This technique is a standard method for solving second-order differential equations in which the independent variable does not appear explicitly. Apply the same method to obtain the solutions of the differential equations
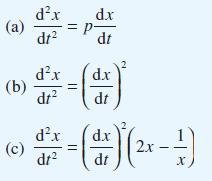
dx (a) x- = dt d.x dt 2 x(0) = 4, dx dt (0) = 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a b c d Hence xp Let v Then This is a separable equation H... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


