Question: 3 In this problem, we explain why the MST algorithm works. Define S = minimum spanning tree Ct = nodes connected after iteration t of
3 In this problem, we explain why the MST algorithm works. Define S = minimum spanning tree Ct = nodes connected after iteration t of MST algorithm has been completed Ct= nodes not connected after iteration t of MST algorithm has been completed At = set of arcs in minimum spanning tree after t iterations of MST algorithm have been completed
Suppose the MST algorithm does not yield a minimum spanning tree. Then, for some t, it must be the case that all arcs in At1 are in S, but the arc chosen at iteration t (call it at) of the MST algorithm is not in S. Then S must contain some arc at that leads from a node in Ct1 to a node in Ct1).
Show that by replacing arc at with arc at, we can obtain a shorter spanning tree than S. This contradiction proves that all arcs chosen by the MST algorithm must be in S. Thus, the MST algorithm does indeed find a minimum spanning tree.
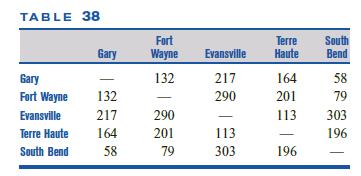
TABLE 38 Fort Terre South Gary Wayne Evansville Haute Bend Gary 132 217 Fort Wayne 132 290 Evansville 217 290 Terre Haute 164 201 113 South Bend 58 79 303 164 58 201 79 113 303 196 196
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


