Question: Consider a system of linear inequalities Ax b, with A R m,n , where a i T , i = 1, . .
Consider a system of linear inequalities Ax ≤ b, with A ∈ Rm,n, where aiT , i = 1, . . . ,m, denote the rows of A, which are assumed, without loss of generality, to be nonzero. Each inequality aTi x ≤ bi can be normalized by dividing both terms by ![]() , hence we shall further assume without loss of generality that
, hence we shall further assume without loss of generality that ![]() Consider now the case when the polyhedron described by these inequalities,
Consider now the case when the polyhedron described by these inequalities, ![]() is nonempty, that is, there exist at least a point
is nonempty, that is, there exist at least a point ![]() In order to find a feasible point (i.e., a point in P), we propose the following simple algorithm. Let k denote the iteration number and initialize the algorithm with any initial point
In order to find a feasible point (i.e., a point in P), we propose the following simple algorithm. Let k denote the iteration number and initialize the algorithm with any initial point![]() holds for all i = 1, . . . ,m, then we found the desired point, hence we return xk, and finish. If instead there exist ik such that aikT xk > bik , then we set
holds for all i = 1, . . . ,m, then we found the desired point, hence we return xk, and finish. If instead there exist ik such that aikT xk > bik , then we set 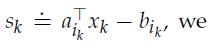 we update36 the current point as
we update36 the current point as
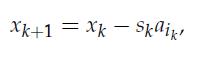
and we iterate the whole process.
1. Give a simple geometric interpretation of this algorithm.
2. Prove that this algorithm either finds a feasible solution in a finite number of iterations, or it produces a sequence of solutions {xk} that converges asymptotically (i.e., for k → ∞) to a feasible solution (if one exists).
3. The problem of finding a feasible solution for linear inequalities can be also put in relation with the minimization of the nonsmooth function ![]() Develop a sub gradient type algorithm for this version of the problem, discuss hypotheses that need be assumed to guarantee convergence, and clarify the relations and similarities with the previous algorithm.
Develop a sub gradient type algorithm for this version of the problem, discuss hypotheses that need be assumed to guarantee convergence, and clarify the relations and similarities with the previous algorithm.
||ai||2,
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 The iterate x k s k ai k simply takes point x k who violates the i k th constraint and projects it back onto the hyperplane Indeed s k a ik T x k b ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


