Question: In the atom interferometer experiment of Figure 38.13 , lasercooling techniques were used to cool a dilute vapor of sodium atoms to a temperature of
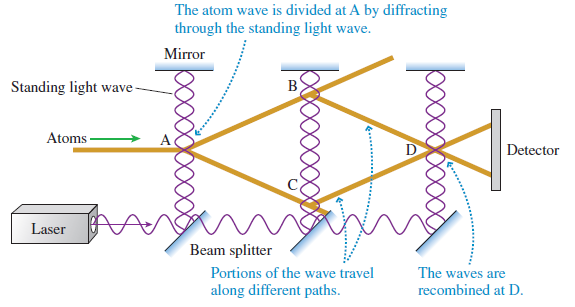
In the atom interferometer experiment ofFigure 38.13, lasercooling techniques were used to cool a dilute vapor of sodium atoms to a temperature of 0.0010 K = 1.0 mK. The ultracold atoms passed through a series of collimating apertures to form the atomic beam you see entering the figure from the left. The standing light waves were created from a laser beam with a wavelength of 590 nm.
a. What is the rms speed vrms of a sodium atom (A = 23) in a gas at temperature 1.0 mK?
b. By treating the laser beam as if it were a diffraction grating, calculate the first-order diffraction angle of a sodium atom traveling with the rms speed of part a.
c. How far apart are points B and C if the second standing wave is 10 cm from the first?
d. Because interference is observed between the two paths, each individual atom is apparently present at both point B and point C. Describe, in your own words, what this experiment tells you about the nature of matter
The atom wave is divided at A by diffracting through the standing light wave. Mirror Standing light wave- Atoms- Detector Laser Beam splitter Portions of the wave travel The waves are along different paths. recombined at D. 6... 000
Step by Step Solution
3.34 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Solve a From Chapter 20 the rms speed of the sodium atom is b The diffraction of a wave by a grating ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (2 attachments)
1442_6054778bec165_700698.pdf
180 KBs PDF File
1442_6054778bec165_700698.docx
120 KBs Word File


