Question: Perform a study of Shellsort, using different increments. Compare the version shown in Section 7.3 , where each increment is half the previous one, with
Perform a study of Shellsort, using different increments. Compare the version shown in Section 7.3 , where each increment is half the previous one, with others. In particular, try implementing “division by 3” where the increments on a list of length n will be n=3, n=9, etc. Do other increment schemes work as well?

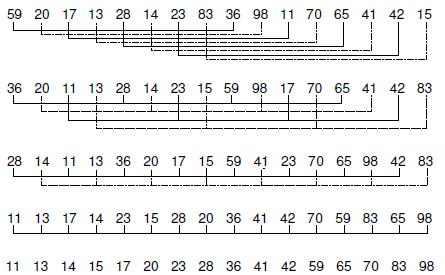
7.3 Shellsort The next sort we consider is called Shellsort, named after its inventor, D.L. Shell. It is also sometimes called the diminishing increment sort. Unlike Insertion and Selection Sort, there is no real life intuitive equivalent to Shellsort. Unlike the exchange sorts, Shellsort makes comparisons and swaps between non-adjacent el- ements. Shellsort also exploits the best-case performance of Insertion Sort. Shell- sort's strategy is to make the list "mostly sorted" so that a final Insertion Sort can finish the job. When properly implemented, Shellsort will give substantially better performance than (n) in the worst case. Shellsort uses a process that forms the basis for many of the sorts presented in the following sections: Break the list into sublists, sort them, then recombine the sublists. Shellsort breaks the array of elements into "virtual" sublists. Each sublist is sorted using an Insertion Sort. Another group of sublists is then chosen and sorted, and so on. During each iteration, Shellsort breaks the list into disjoint sublists so that each element in a sublist is a fixed number of positions apart. For example, let us as- sume for convenience that n, the number of values to be sorted, is a power of two. One possible implementation of Shellsort will begin by breaking the list into n/2 sublists of 2 elements each, where the array index of the 2 elements in each sublist differs by n/2. If there are 16 elements in the array indexed from 0 to 15, there would initially be 8 sublists of 2 elements each. The first sublist would be the ele- ments in positions 0 and 8, the second in positions 1 and 9, and so on. Each list of two elements is sorted using Insertion Sort.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Java import javautilArrays public class ShellsortComparison public static void mainString args int a... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


