An antibiotic is administered intravenously into the bloodstream at a constant rate r. As the drug flows
Question:
An antibiotic is administered intravenously into the bloodstream at a constant rate r. As the drug flows through the patient’s system and acts on the infection that is present, it is removed from the bloodstream at a rate proportional to the amount in the bloodstream at that time. Since the amount of blood in the patient is constant, this means that the concentration y = y(t) of the antibiotic in the bloodstream can be modeled by the differential equation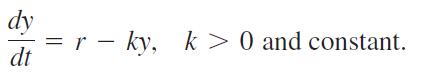
a. If y(0) = y0, find the concentration y(t) at any time t.
b. Assume that y0y→∞ y(t). Sketch the solution curve for the concentration.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Thomas Calculus Early Transcendentals
ISBN: 9780321884077
13th Edition
Authors: Joel R Hass, Christopher E Heil, Maurice D Weir
Question Posted:





