Question: In Example 2 we represented the function (x) = 2/x as a power series about x = 2. Use a geometric series to represent (x)
In Example 2 we represented the function ƒ(x) = 2/x as a power series about x = 2. Use a geometric series to represent ƒ(x) as a power series about x = 1, and find its interval of convergence.
In Example 2
In Equation 2
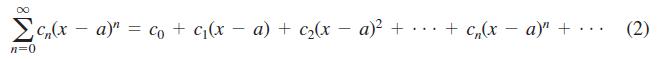
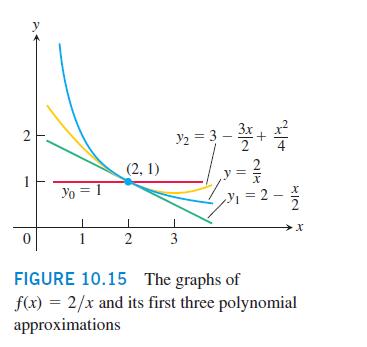
for SO matches This is a geometric series with first term 1 and ratio r = - X 2 2 The power series - 1 12 (x 2) + (x 2) + ... + Equation (2) with a = 2, co = 1, = -1/2, C = 1/4,..., C = (-1/2)". The series converges X 2 2 = 1 < 1 or 0 < x < 4. The sum is (x - 2) 2 1 + (x - 2) 4 r 1 + + (-1)*(x 1 X - 2 2 n + (-1)'x Series (4) generates useful polynomial approximations of f(x) = 2/x for values of x near 2: || Po(x) = 1 X P(x) = 1 - (x 2) = 2 - 1/2 X' 2)" + (x - 2) + P(x) = 1 - - 1/2 (x 2) + 1/ (x 2) = 3 - - (4) + x 0 < x < 4. and so on (Figure 10.15). The following example illustrates how we test a power series for convergence by using the Ratio Test to see where it converges and diverges.
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To represent the function x 2x as a power series about x 1 we use the formula ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


