Question: Complete the approximation argument for Lvy's arc-sine law from (S 8.9) : a) Show, by a direct calculation, that (v_{n, lambda}(x)) converges as (n
Complete the approximation argument for Lévy's arc-sine law from \(\S 8.9\) :
a) Show, by a direct calculation, that \(v_{n, \lambda}(x)\) converges as \(n \rightarrow \infty\). Conclude from (8.16) that \(v_{n, \lambda}^{\prime \prime}\) converges.
b) Integrate the ODE (8.16) to see that \(v_{n, \lambda}(x)-v_{n, \lambda}^{\prime}(0)\) has a limit. Integrating once again shows that \(v_{n, \lambda}^{\prime}(0)\) converges, too.
c) Identify the limits of \(v_{n, \lambda}, v_{n, \lambda}^{\prime}\) and \(v_{n, \lambda}^{\prime \prime}\).
Data From Equation (8.16)
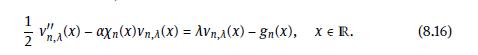
1 vn, (x) - axn(x)vn,(x) = AVn,(x)-gn(x), x = R. (8.16)
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (144 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


