Question: Define the stochastic process ({X(t), t in mathbf{R}}) by [X(t)=A cos (omega t+Phi)] where (A) and (Phi) are independent random variables with (E(A)=0) and (Phi)
Define the stochastic process \(\{X(t), t \in \mathbf{R}\}\) by
\[X(t)=A \cos (\omega t+\Phi)\]
where \(A\) and \(\Phi\) are independent random variables with \(E(A)=0\) and \(\Phi\) is uniformly distributed over the interval \([0,2 \pi]\).
Check whether the covariance function of the weakly stationary process \(\{X(t), t \in \mathbf{R}\}\) can be obtained from the limit relation (12.5).
The covariance function of a slightly more general process has been determined in example 6.6 at page 235 .
Data from Example 6.6
In modifying example 6.3, let
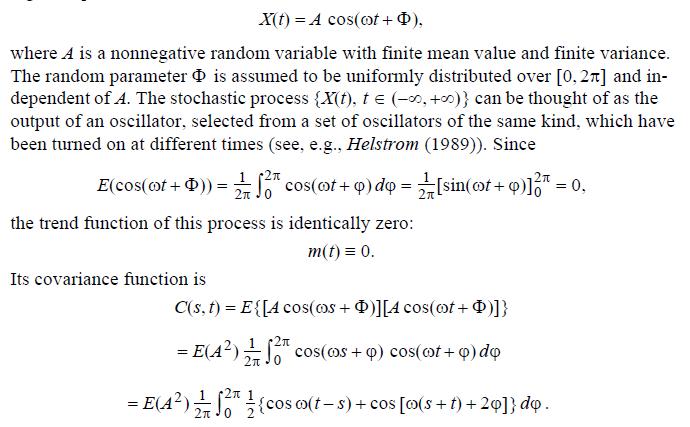
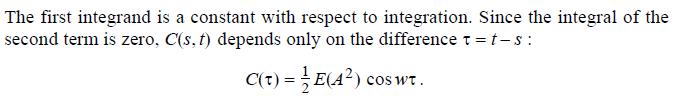
Thus, the process is weakly stationary.
Data from 12.5
![be uniformly distributed over [0,2] and in- dependent of A. The stochastic](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1714/0/3/2/324662a0ec42351c1714075492808.jpg)
X(t) = A cos(cot+). where A is a nonnegative random variable with finite mean value and finite variance. The random parameter is assumed to be uniformly distributed over [0,2] and in- dependent of A. The stochastic process {X(t), t = (-0, +0)} can be thought of as the output of an oscillator, selected from a set of oscillators of the same kind, which have been turned on at different times (see, e.g., Helstrom (1989)). Since E(cos(ot+)) = cos(ot+ q) do = 2 [sin(ot + q)] = 0, 1 2 2 JO the trend function of this process is identically zero: 2 Its covariance function is m(t) = 0. C(s, t) E{[A cos(s+)][A cos(oot+)]} 2 = E(A) + cos(cos + q) cos(ot+ q) do 2 = E(A){cos (t s) + cos [o(s+t) + 2]} do.
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


