Question: 1 . 3 3 Spread spectrum communication systems reduce the effects of narrow bandwidth interference by spreading the bandwidth of the transmitted signal out over
Spread spectrum communication systems reduce the effects of narrow bandwidth
interference by spreading the bandwidth of the transmitted signal out over a range
of frequencies much greater than the bandwidth occupied by an AMDSBSC signal
alone. Consider the AMDSBSC signal in Eq where is the message
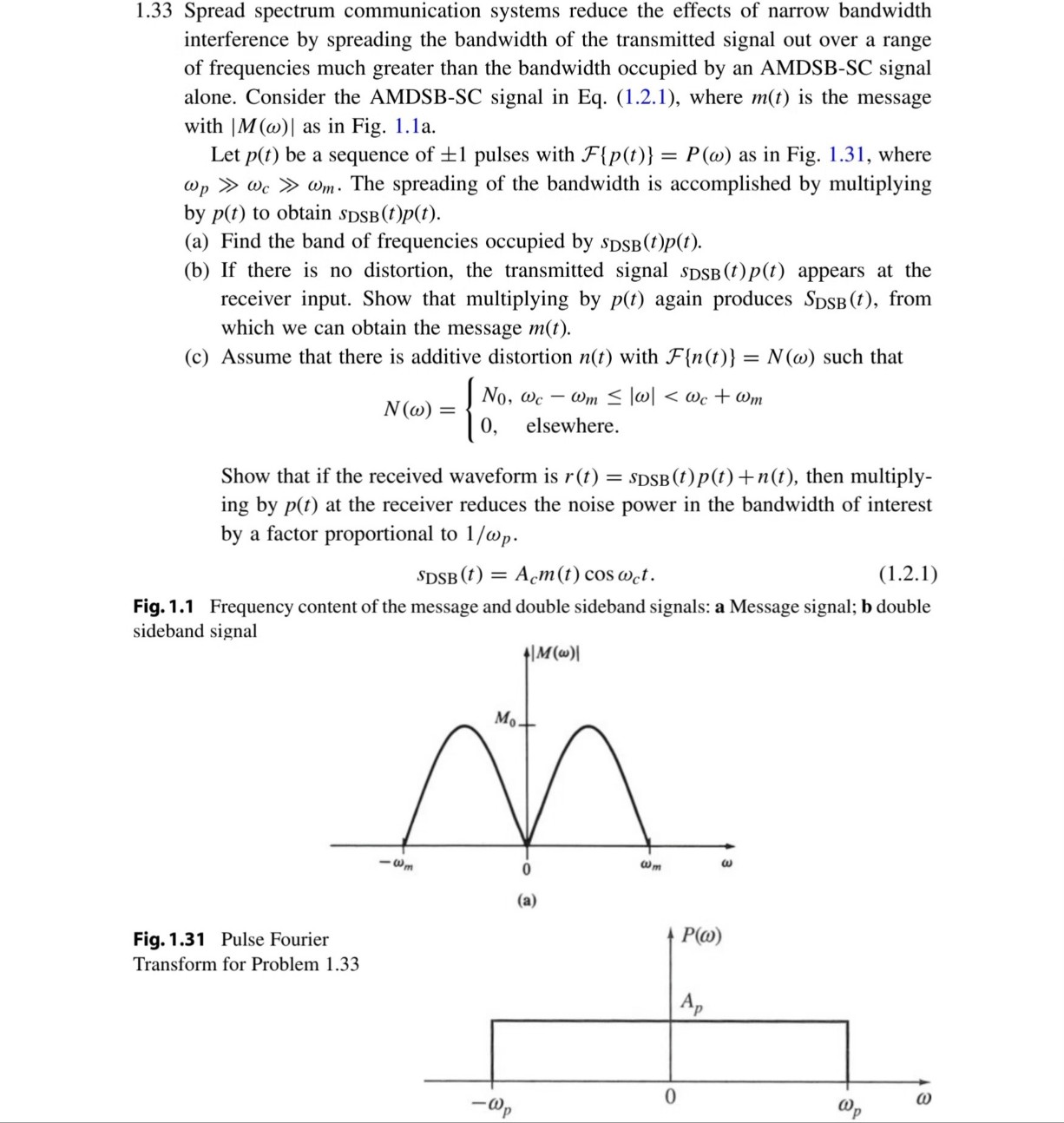
with as in Fig. a
Let be a sequence of pulses with as in Fig. where
The spreading of the bandwidth is accomplished by multiplying
by to obtain
a Find the band of frequencies occupied by
b If there is no distortion, the transmitted signal appears at the
receiver input. Show that multiplying by again produces from
which we can obtain the message
c Assume that there is additive distortion with such that
Show that if the received waveform is then multiply
ing by at the receiver reduces the noise power in the bandwidth of interest
by a factor proportional to
Fig. Frequency content of the message and double sideband signals: a Message signal; double
sideband signal
Fig. Pulse Fourier
Transform for Problem
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


