Question: 1. A rectangular block of height L and horizontal cross-sectional area A floats at the interface between two immiscible liquids, as shown below. a. Derive
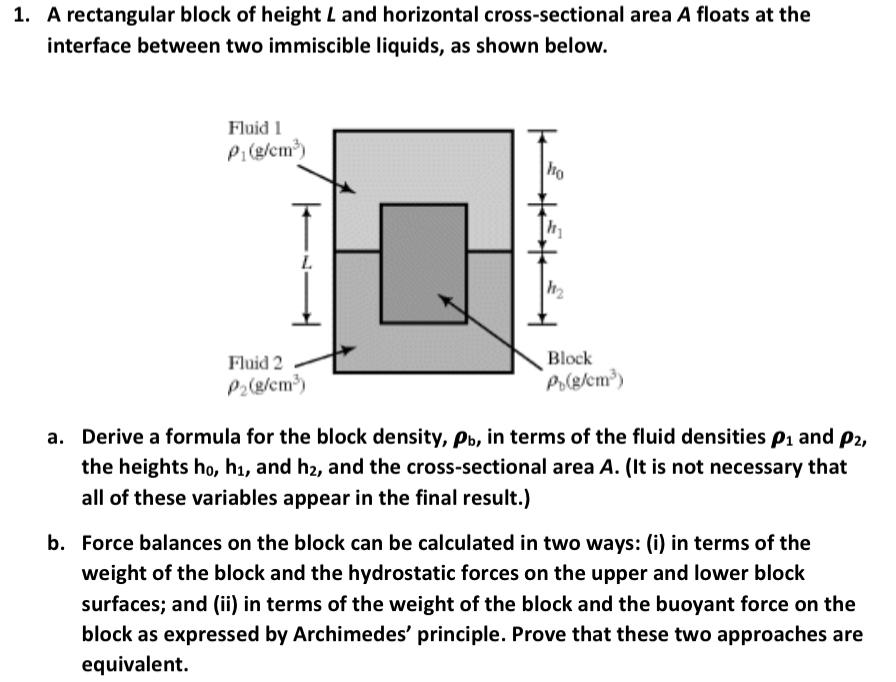
1. A rectangular block of height L and horizontal cross-sectional area A floats at the interface between two immiscible liquids, as shown below. a. Derive a formula for the block density, b, in terms of the fluid densities 1 and 2, the heights h0,h1, and h2, and the cross-sectional area A. (It is not necessary that all of these variables appear in the final result.) b. Force balances on the block can be calculated in two ways: (i) in terms of the weight of the block and the hydrostatic forces on the upper and lower block surfaces; and (ii) in terms of the weight of the block and the buoyant force on the block as expressed by Archimedes' principle. Prove that these two approaches are equivalent. 1. A rectangular block of height L and horizontal cross-sectional area A floats at the interface between two immiscible liquids, as shown below. a. Derive a formula for the block density, b, in terms of the fluid densities 1 and 2, the heights h0,h1, and h2, and the cross-sectional area A. (It is not necessary that all of these variables appear in the final result.) b. Force balances on the block can be calculated in two ways: (i) in terms of the weight of the block and the hydrostatic forces on the upper and lower block surfaces; and (ii) in terms of the weight of the block and the buoyant force on the block as expressed by Archimedes' principle. Prove that these two approaches are equivalent
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


