Question: 1. Arrow-Pratt Risk Aversion Recall the formula for Absolute Risk Aversion (ARA) and Relative Risk Aversion (RRA) ARA = -U(x)/U'(x) RRA = -xU(x)/U'(x) (a) Exponential
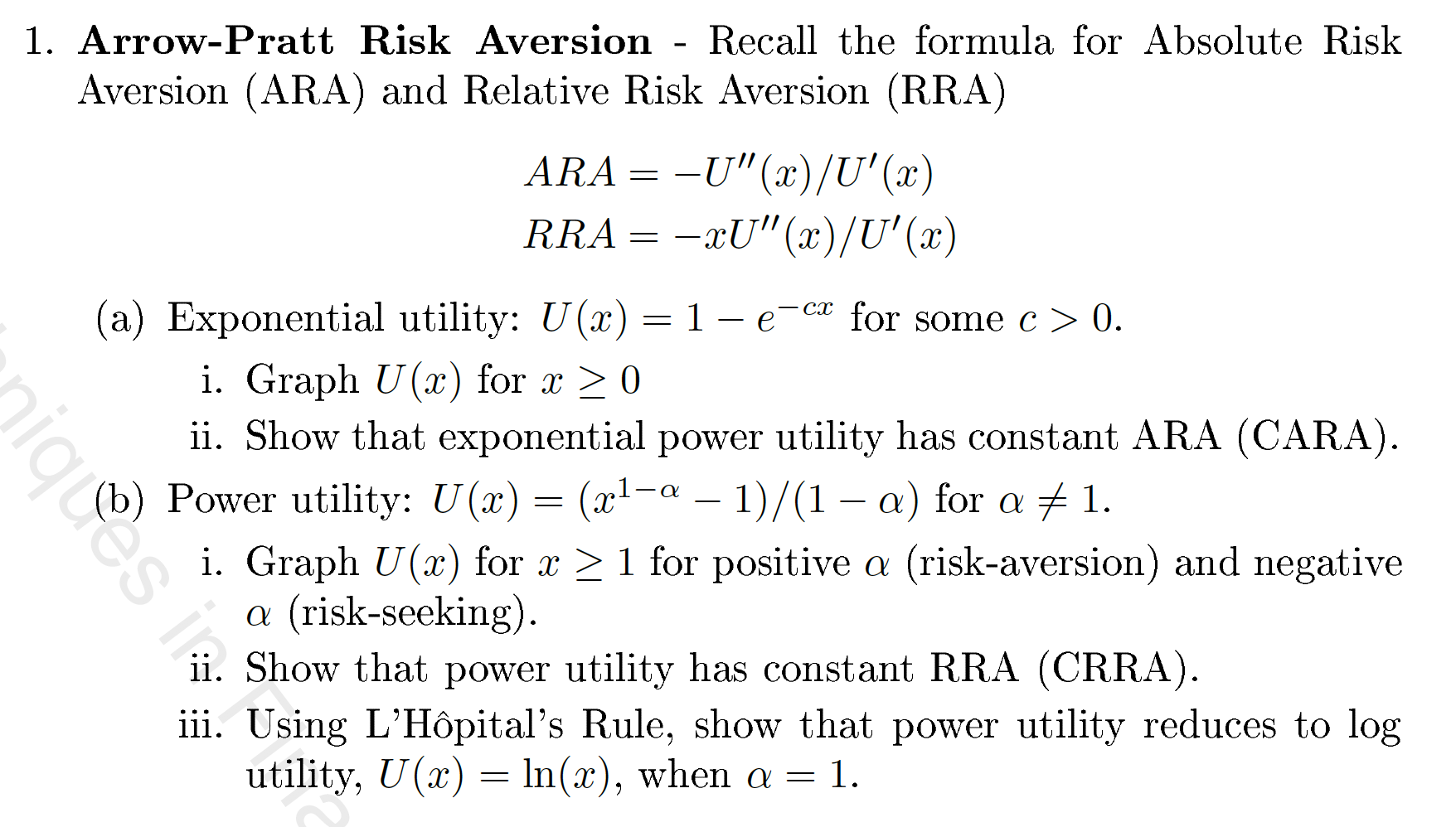
1. Arrow-Pratt Risk Aversion Recall the formula for Absolute Risk Aversion (ARA) and Relative Risk Aversion (RRA) ARA = -U"(x)/U'(x) RRA = -xU"(x)/U'(x) (a) Exponential utility: U(X) = 1-e-cx for some c > 0. i. Graph U(x) for x > 0 ii. Show that exponential power utility has constant ARA (CARA). Power utility: U(x) = (x1-a 1)/(1 a) for a + 1. i. Graph U(x) for x > 1 for positive a (risk-aversion) and negative a (risk-seeking). ii. Show that power utility has constant RRA (CRRA). iii. Using L'Hpital's Rule, show that power utility reduces to log utility, U(x) = ln(x), when a = 1. 1. Arrow-Pratt Risk Aversion Recall the formula for Absolute Risk Aversion (ARA) and Relative Risk Aversion (RRA) ARA = -U"(x)/U'(x) RRA = -xU"(x)/U'(x) (a) Exponential utility: U(X) = 1-e-cx for some c > 0. i. Graph U(x) for x > 0 ii. Show that exponential power utility has constant ARA (CARA). Power utility: U(x) = (x1-a 1)/(1 a) for a + 1. i. Graph U(x) for x > 1 for positive a (risk-aversion) and negative a (risk-seeking). ii. Show that power utility has constant RRA (CRRA). iii. Using L'Hpital's Rule, show that power utility reduces to log utility, U(x) = ln(x), when a = 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


