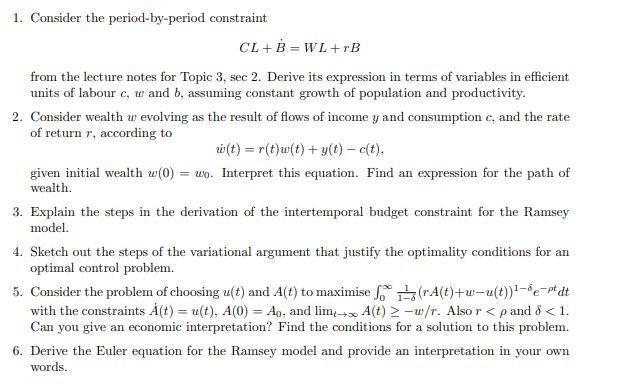
Question: . 1. Consider the period-by-period constraint CL + B = WL+rB from the lecture notes for Topic 3, sec 2. Derive its expression in terms
.
1. Consider the period-by-period constraint CL + B = WL+rB from the lecture notes for Topic 3, sec 2. Derive its expression in terms of variables in efficient units of labour c, w and b, assuming constant growth of population and productivity. 2. Consider wealth w evolving as the result of flows of income y and consumption c, and the rate of return r, according to i(t) = r(t)w(t) + y(t) e(t), given initial wealth w(0) = wo. Interpret this equation. Find an expression for the path of wealth. 3. Explain the steps in the derivation of the intertemporal budget constraint for the Ramsey model. 4. Sketch out the steps of the variational argument that justify the optimality conditions for an optimal control problem. 5. Consider the problem of choosing u(t) and A(t) to maximise A(t)+w-u(t))'-e-t dt with the constraints A(t) = u(t), A(0) = Ao, and lim,- A(t) > -w/r. Also r < p and 8 < 1. Can you give an economic interpretation? Find the conditions for a solution to this problem. %3! 6. Derive the Euler equation for the Ramsey model and provide an interpretation in your own words.
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 The periodbyperiod constraint CLBWLrB can be expressed in terms of variables in efficient units of labour c w and b assuming constant growth of population and productivity as follows c 1 rb w 1 rb T... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


