Question: 1. Overflow condition is checked in the 1-bit ALU for the most significant bit (sign bit). Ainvert Operation Carryin Binvert Overflow cases: 1. adding 2
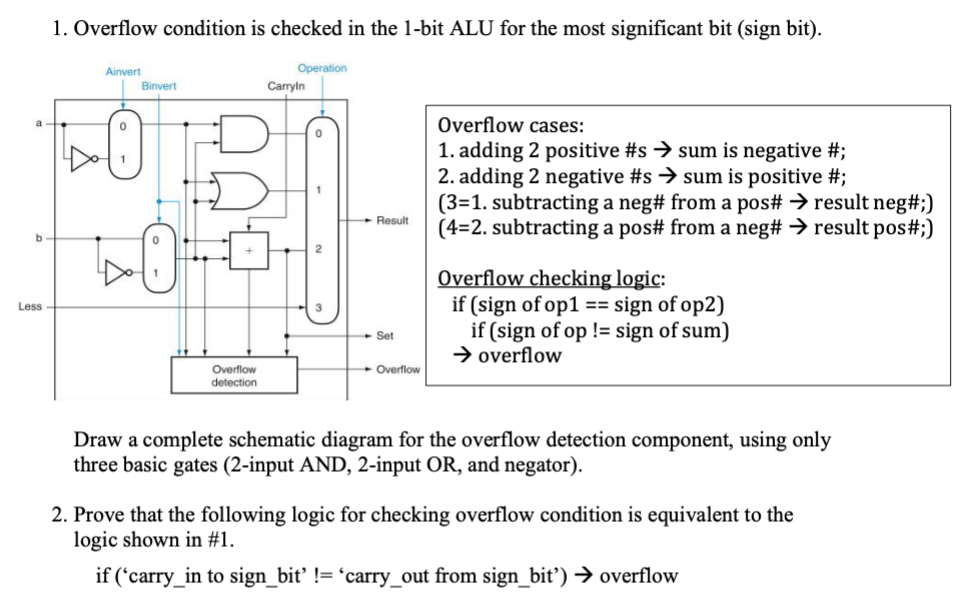
1. Overflow condition is checked in the 1-bit ALU for the most significant bit (sign bit). Ainvert Operation Carryin Binvert Overflow cases: 1. adding 2 positive #s sum is negative #; 2. adding 2 negative #s sum is positive #; (3=1. subtracting a neg# from a pos# result neg#;) (4=2. subtracting a pos# from a neg# result pos#;) 0 20 1 Result Less Overflow checking logic: if (sign of op1 == sign of op2) if (sign of op != sign of sum) overflow Set Overflow detection - Overflow Draw a complete schematic diagram for the overflow detection component, using only three basic gates (2-input AND, 2-input OR, and negator). 2. Prove that the following logic for checking overflow condition is equivalent to the logic shown in #1. if ('carry_in to sign_bi != 'carry out from sign_bit) overflow 1. Overflow condition is checked in the 1-bit ALU for the most significant bit (sign bit). Ainvert Operation Carryin Binvert Overflow cases: 1. adding 2 positive #s sum is negative #; 2. adding 2 negative #s sum is positive #; (3=1. subtracting a neg# from a pos# result neg#;) (4=2. subtracting a pos# from a neg# result pos#;) 0 20 1 Result Less Overflow checking logic: if (sign of op1 == sign of op2) if (sign of op != sign of sum) overflow Set Overflow detection - Overflow Draw a complete schematic diagram for the overflow detection component, using only three basic gates (2-input AND, 2-input OR, and negator). 2. Prove that the following logic for checking overflow condition is equivalent to the logic shown in #1. if ('carry_in to sign_bi != 'carry out from sign_bit) overflow
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


