Question: 1. Transition between B and S form DNA jected to a stretching force exceeding 60 pN undergoes a structural transition from the usual B he
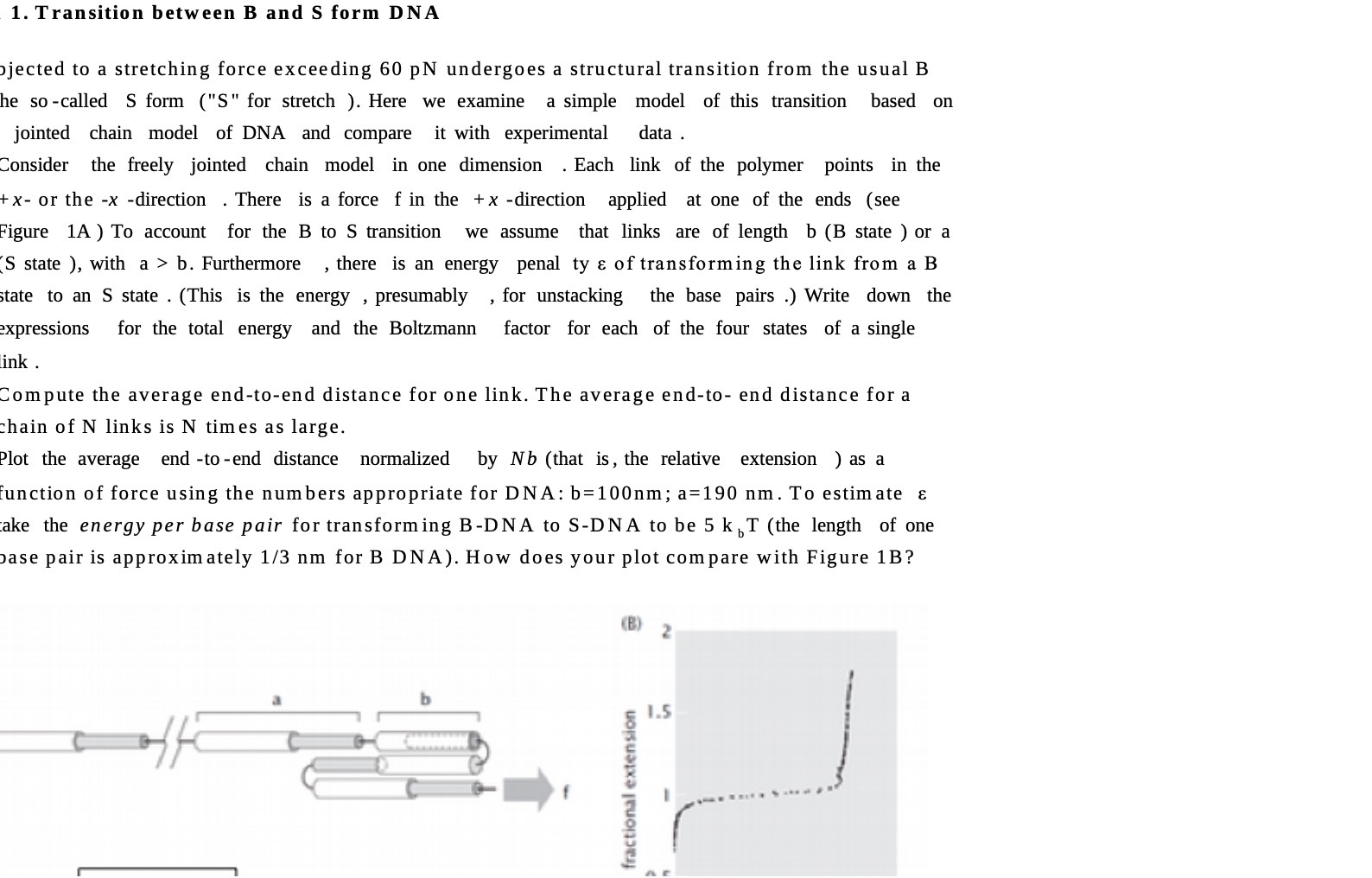
1. Transition between B and S form DNA jected to a stretching force exceeding 60 pN undergoes a structural transition from the usual B he so-called S form ("'S" for stretch ). Here we examine a simple model of this transition based on jointed chain model of DNA and compare it with experimental data . Consider the freely jointed chain model in one dimension . Each link of the polymer points in the + x- or the -x -direction . There is a force f in the + x -direction applied at one of the ends (see "igure 1A ) To account for the B to S transition we assume that links are of length b (B state ) or a S state ), with a > b. Furthermore , there is an energy penal ty & of transforming the link from a B state to an S state . (This is the energy , presumably , for unstacking the base pairs .) Write down the xpressions for the total energy and the Boltzmann factor for each of the four states of a single ink . Compute the average end-to-end distance for one link. The average end-to- end distance for a hain of N links is N times as large. Plot the average end -to-end distance normalized by Nb (that is, the relative extension ) as a function of force using the numbers appropriate for DNA: b=100nm; a=190 nm. To estimate & ake the energy per base pair for transforming B-DNA to S-DNA to be 5 k , T (the length of one base pair is approximately 1/3 nm for B DNA). How does your plot compare with Figure 1B? (B) 2 1.5 fractional extension
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


