Question: 1. Type in program 2.32, studentPtr.cpp and run the program. Identify how pointer of object is implemented in the program. Change main () program

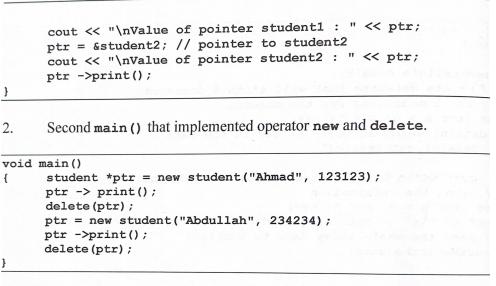
1. Type in program 2.32, studentPtr.cpp and run the program. Identify how pointer of object is implemented in the program. Change main () program to the second example. The second main () program create object using new operator and destroy the object using delete. Identify the difference of the methods used in the first main () and the second main(). // Program 2.32 // studentPtr.cpp - pointer to object #include #include using namespace std; class Student ( private: string studentName; unsigned long netrico; public: Student (string na, unsigned long no) (metricko no; studentNamena: } void print () I cout < < " Student's Name: " < < studentName: cout < < " Student's Metric Number:" < < metrico; } 12 void main() f student studenti ("Ahmad", 123123); // objek Student student student2 ("Abdullah", 234234): cout < < " Address of the object " cout < < " Address of studenti: " < 2. cout < < " Value of pointer student1: ptr=&student2; // pointer to student2 cout < < " Value of pointer student2: ptr ->print(); " < < ptr; " < < ptr; Second main() that implemented operator new and delete. void main() { student *ptr = new student ("Ahmad", 123123); ptr>print(); delete (ptr); ptr = new student ("Abdullah", 234234); ptr ->print(); delete (ptr); 1. Type in program 2.32, studentPtr.cpp and run the program. Identify how pointer of object is implemented in the program. Change main () program to the second example. The second main () program create object using new operator and destroy the object using delete. Identify the difference of the methods used in the first main () and the second main(). // Program 2.32 // studentPtr.cpp - pointer to object #include #include using namespace std; class Student ( private: string studentName; unsigned long netrico; public: Student (string na, unsigned long no) (metricko no; studentNamena: } void print () I cout < < " Student's Name: " < < studentName: cout < < " Student's Metric Number:" < < metrico; } 12 void main() f student studenti ("Ahmad", 123123); // objek Student student student2 ("Abdullah", 234234): cout < < " Address of the object " cout < < " Address of studenti: " < 2. cout < < " Value of pointer student1: ptr=&student2; // pointer to student2 cout < < " Value of pointer student2: ptr ->print(); " < < ptr; " < < ptr; Second main() that implemented operator new and delete. void main() { student *ptr = new student ("Ahmad", 123123); ptr>print(); delete (ptr); ptr = new student ("Abdullah", 234234); ptr ->print(); delete (ptr); 1. Type in program 2.32, studentPtr.cpp and run the program. Identify how pointer of object is implemented in the program. Change main () program to the second example. The second main () program create object using new operator and destroy the object using delete. Identify the difference of the methods used in the first main () and the second main(). // Program 2.32 // studentPtr.cpp - pointer to object #include #include using namespace std; class Student ( private: string studentName; unsigned long netrico; public: Student (string na, unsigned long no) (metricko no; studentNamena: } void print () I cout < < " Student's Name: " < < studentName: cout < < " Student's Metric Number:" < < metrico; } 12 void main() f student studenti ("Ahmad", 123123); // objek Student student student2 ("Abdullah", 234234): cout < < " Address of the object " cout < < " Address of studenti: " < 2. cout < < " Value of pointer student1: ptr=&student2; // pointer to student2 cout < < " Value of pointer student2: ptr ->print(); " < < ptr; " < < ptr; Second main() that implemented operator new and delete. void main() { student *ptr = new student ("Ahmad", 123123); ptr>print(); delete (ptr); ptr = new student ("Abdullah", 234234); ptr ->print(); delete (ptr);
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The program given in the question is in C programming language and asked that what is the difference ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


